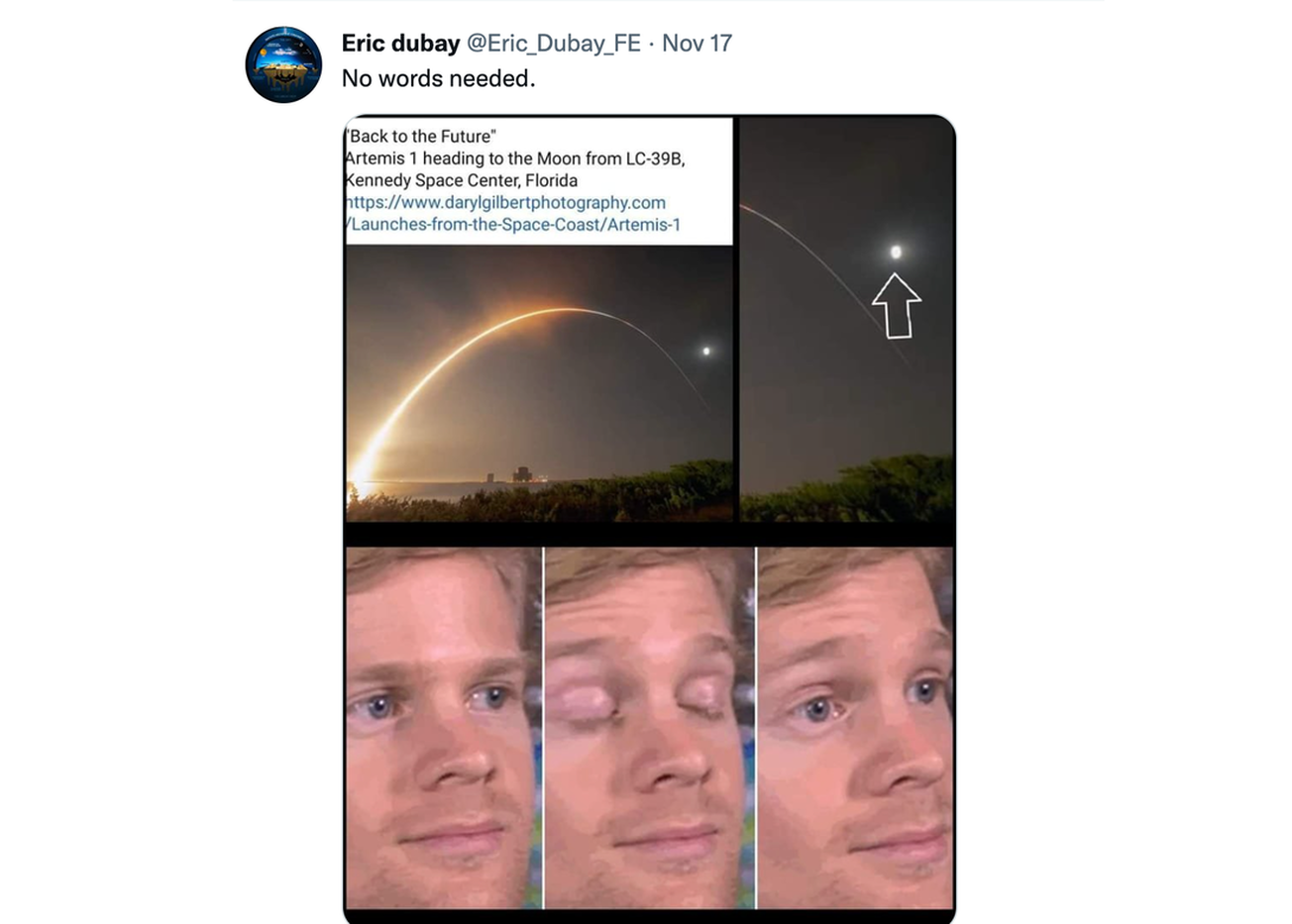
Some things Artemis Launch Showed Us
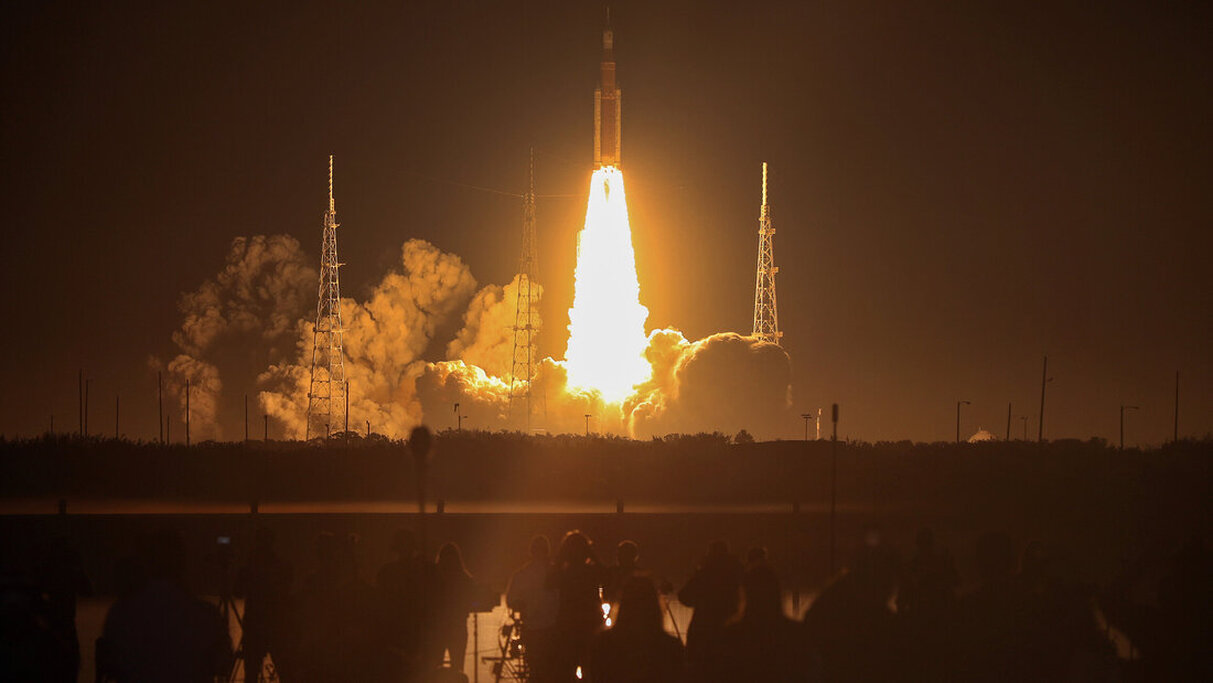
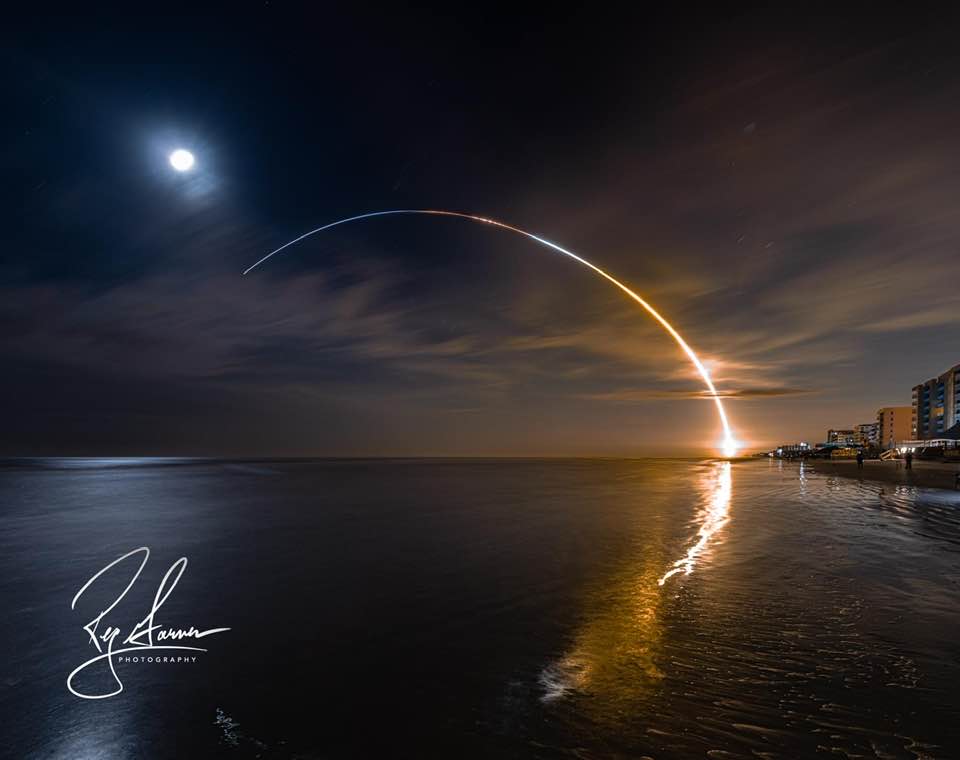
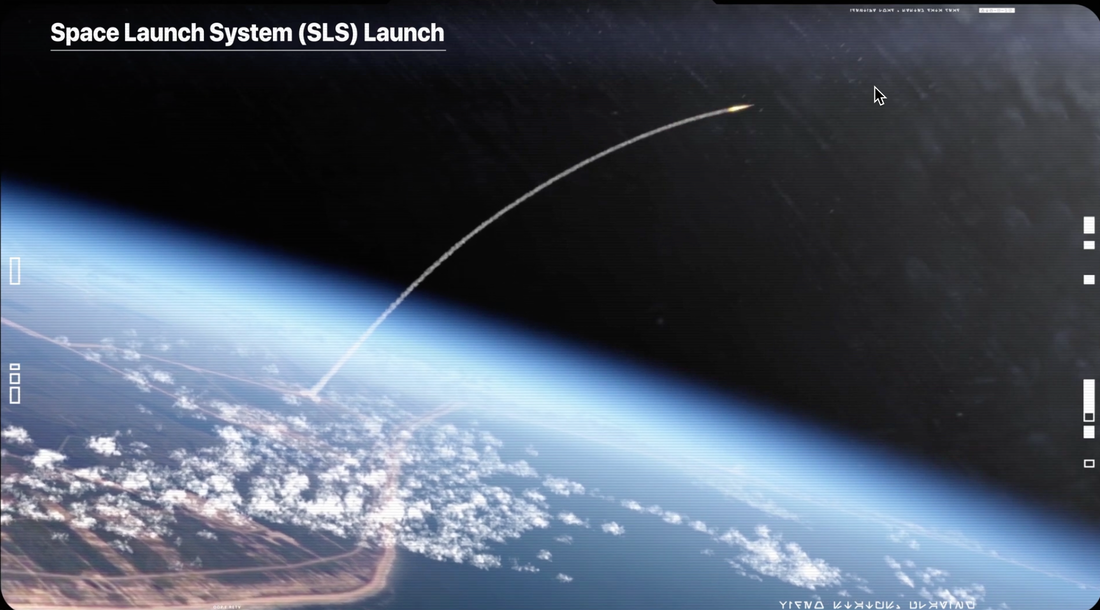
1. Artemis Launch Seen by thousands
2. Staging seen by many and happened as NASA claimed
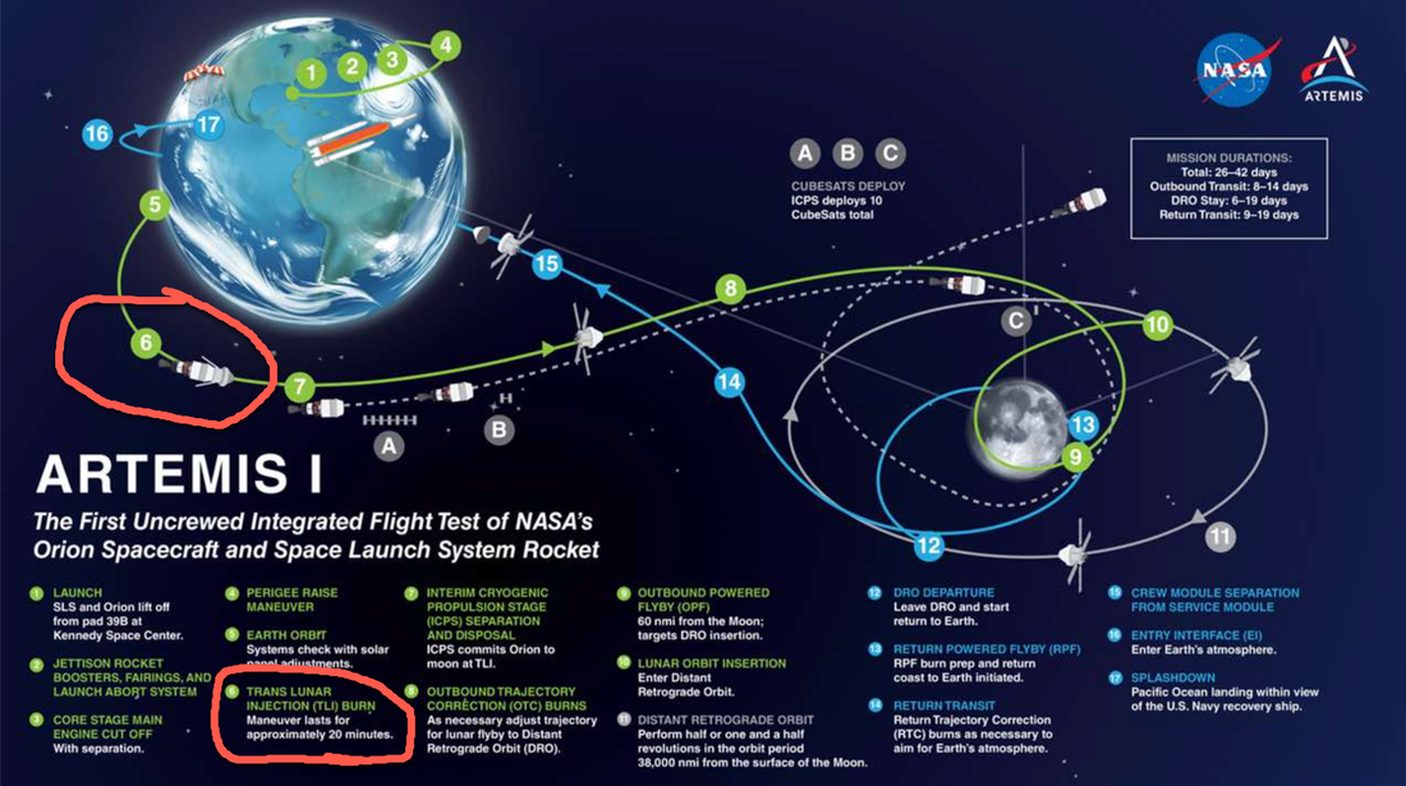
3. Trajectory followed to get to the moon in 3 days
4. Orbital Mechanics on earth demonstrated with requisite velocity
Came back around 1:50 later
5. Space Exists, there is no dome
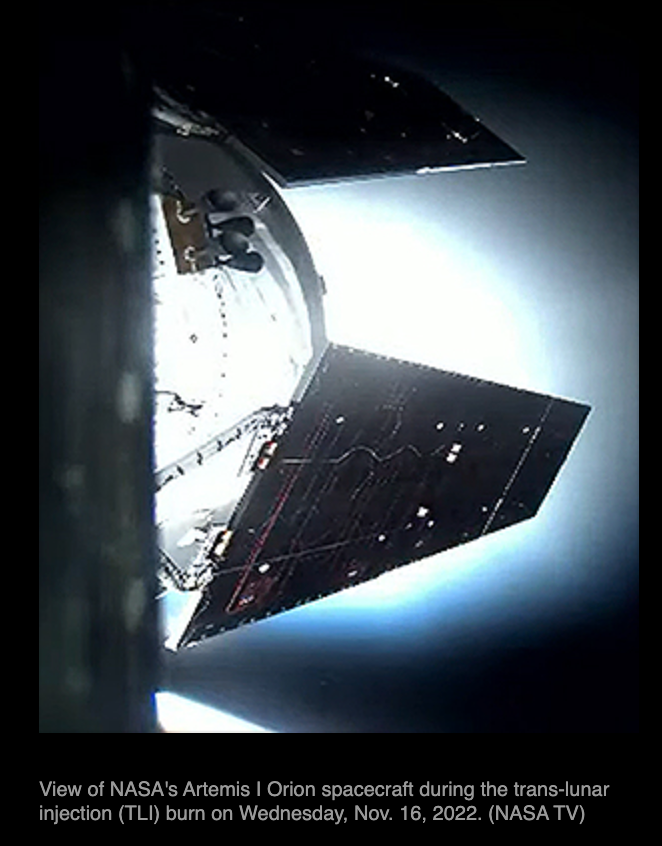
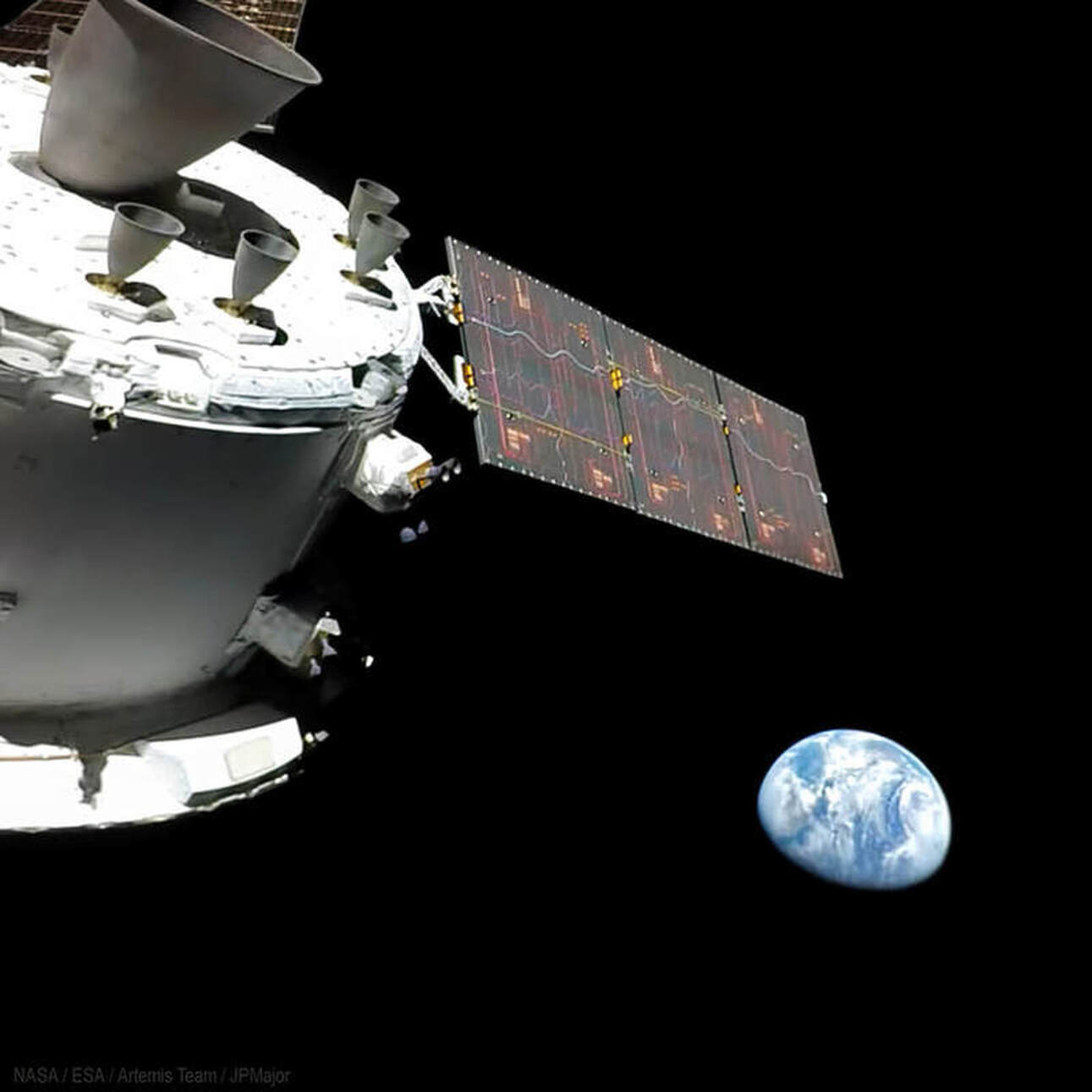
6. Showed on to moon a day later
7. Rockets work just fine in space
5.75 million pounds
9 million points of thrust
322 feet tall.
Most powerful rocket ever built by NASA
Launched 1:47 am this morning November 16th
First Human Rated Spacecraft capturing Images of earth since 1972
1. Artemis Launch Seen by thousands
2. Staging seen by many and happened as NASA claimed
3. Trajectory followed to get to the moon in 3 days
4. Orbital Mechanics on earth demonstrated with requisite velocity
Came back around 1:50 later
5. Space Exists, there is no dome
6. Showed on to moon a day later
7. Rockets work just fine in space
5.75 million pounds
9 million points of thrust
322 feet tall.
Most powerful rocket ever built by NASA
Launched 1:47 am this morning November 16th
First Human Rated Spacecraft capturing Images of earth since 1972
|
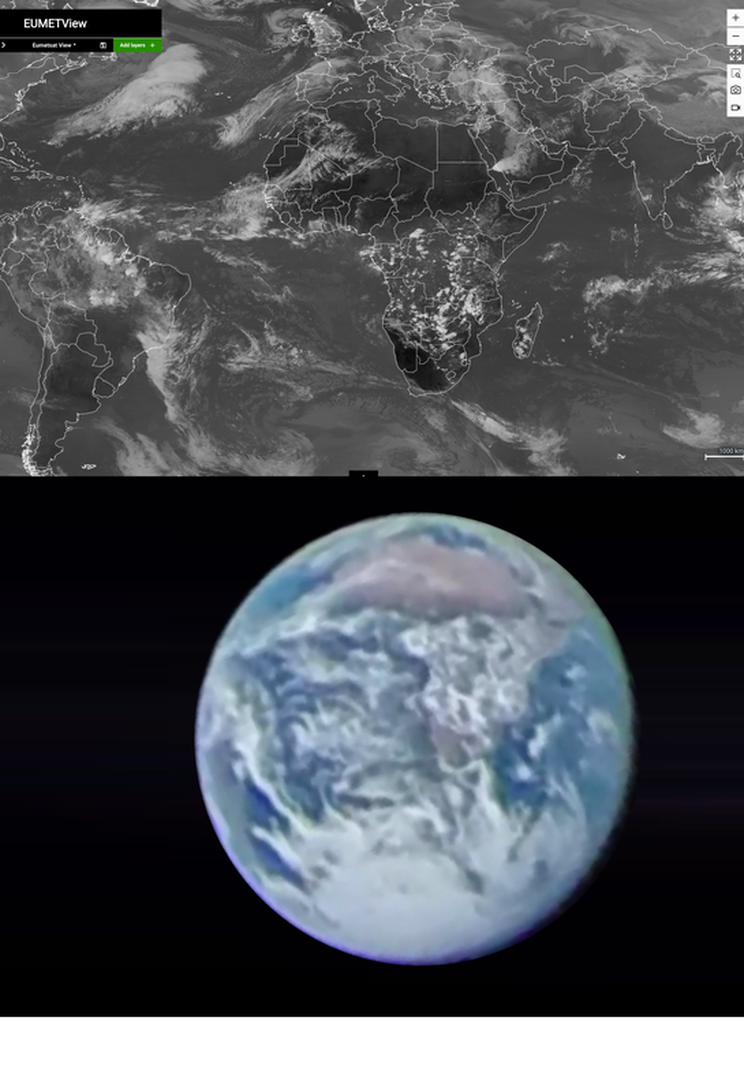
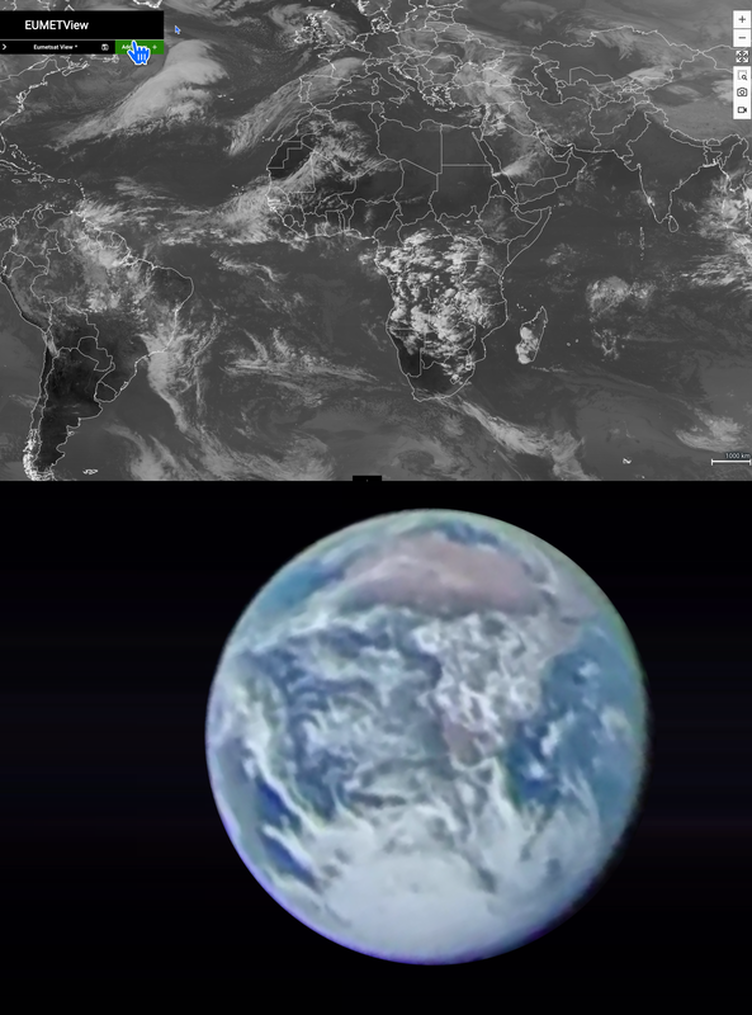
12 Noon UTC Thursday November 24th
Meteosat Satelite Images. Look closely at fainter clouds they do match! (It helps to turn up brightness on your screen) |
3pm UTC Thursday November 24th
Meteosat Satelite Images. Look closely at fainter clouds they do match! (It helps to turn up brightness on your screen) |
3. Trajectory followed to get to the moon in 3 days
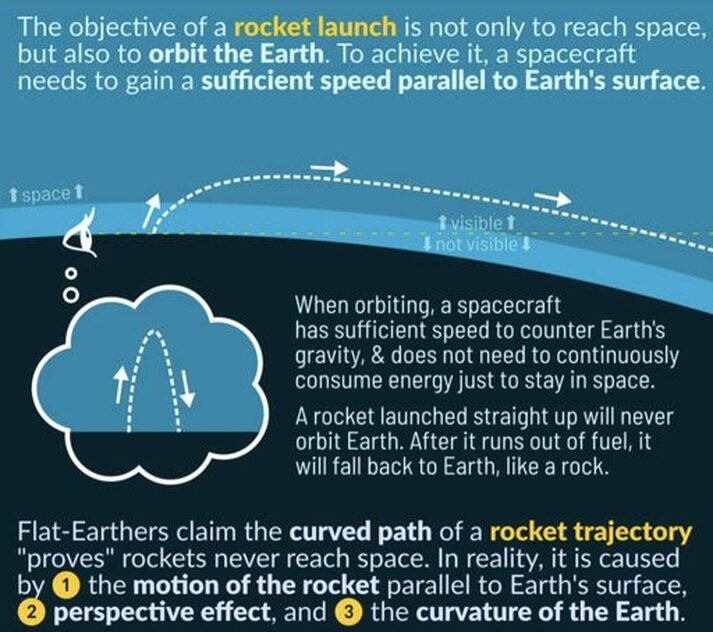
This flight path can be rationally explained:
1) Rocket launches have a curved trajectory because their objective is not only to reach space but also to enter Earth orbit. To achieve it, a spacecraft needs to gain a sufficient horizontal speed, parallel to Earth’s surface.
2) The most efficient way to reach orbit is to initially travel straight up to overcome air resistance, then tilt onto its side and gradually increase this tilt until the rocket is parallel to Earth’s surface.
3) ===> If the rocket launches straight up, it will reach space faster with less energy. But it will not have the required velocity to orbit. The rocket will have to continuously spend energy only to remain up there. Once it runs out of fuel, the rocket will fall back to the Earth very fast. It’s not rocket science.
4) From the vantage point of an observer near the launch location, the rocket will eventually appear to go “down.” It is due to the aforementioned horizontal motion of the rocket: the rocket does not go only up, but also away. The perspective effect also contributes to the observation: the rocket is going farther, and as it goes farther, it will appear closer and closer to the horizon.
5) And last but not least, the rocket follows Earth’s surface, which is curved. The rocket will eventually disappear below the horizon, just like a ship traveling away will start disappearing from the bottom first.
1) Rocket launches have a curved trajectory because their objective is not only to reach space but also to enter Earth orbit. To achieve it, a spacecraft needs to gain a sufficient horizontal speed, parallel to Earth’s surface.
2) The most efficient way to reach orbit is to initially travel straight up to overcome air resistance, then tilt onto its side and gradually increase this tilt until the rocket is parallel to Earth’s surface.
3) ===> If the rocket launches straight up, it will reach space faster with less energy. But it will not have the required velocity to orbit. The rocket will have to continuously spend energy only to remain up there. Once it runs out of fuel, the rocket will fall back to the Earth very fast. It’s not rocket science.
4) From the vantage point of an observer near the launch location, the rocket will eventually appear to go “down.” It is due to the aforementioned horizontal motion of the rocket: the rocket does not go only up, but also away. The perspective effect also contributes to the observation: the rocket is going farther, and as it goes farther, it will appear closer and closer to the horizon.
5) And last but not least, the rocket follows Earth’s surface, which is curved. The rocket will eventually disappear below the horizon, just like a ship traveling away will start disappearing from the bottom first.
4. Orbital Mechanics on earth demonstrated
5. Space Exists, there is no dome
6. Showed on to moon a day later
Images Taken On the Way to the Moon
7. Rockets work just fine in space

**Rocket Science Explained**
For some reason, flat earthers think rockets are impossible because of the lack of air in space. But rocket propulsion is totally different than traditional airplane turbine propulsion, hence the confusion.
Thrust is the force which moves any aircraft through the air. Thrust is generated by the propulsion system of the aircraft. Different propulsion systems develop thrust in different ways, but all thrust is generated through some application of Newton's third law of motion. For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction.
For some reason, flat earthers think rockets are impossible because of the lack of air in space. But rocket propulsion is totally different than traditional airplane turbine propulsion, hence the confusion.
Thrust is the force which moves any aircraft through the air. Thrust is generated by the propulsion system of the aircraft. Different propulsion systems develop thrust in different ways, but all thrust is generated through some application of Newton's third law of motion. For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction.
Consider a cannon. When you shoot a cannonball out of a cannon, the cannonball goes in one direction and the cannon recoils in the opposite direction.
The magnitude of the momentum of the cannonball is equal to the momentum of the recoiled cannon in the opposite direction such that the momentum of the net cannon-cannonball system is net zero.
The magnitude of the momentum of the cannonball is equal to the momentum of the recoiled cannon in the opposite direction such that the momentum of the net cannon-cannonball system is net zero.
Consider a rocket sitting in space, there is next to no momentum in the system. Then the engines ignite and the exhaust gases go in one direction and the rocket goes in the other direction. And this keeps the total momentum of the system constant. The momentum change of the gases gives the rocket the push to go forward, which is called the thrust. Or stated from Newtons 3rd law The EJECTED fuel causes an equal and opposite force in space which is called the thrust. And to ignite the fuel rockets come with a liquid oxygen tank or some oxidizer so that is factored in too.
A general derivation of the thrust equation shows that the amount of thrust generated depends on the mass flow through the engine and the exit velocity of the gas.
When a rocket shoots fuel out one end, this propels the rocket forward — no air is required.
In a rocket engine , fuel and a source of oxygen, called an oxidizer, are mixed and exploded in a combustion chamber. The combustion produces hot exhaust which is passed through a nozzle to accelerate the flow and produce thrust.
Turbine engines and propellers use air from the atmosphere as the working fluid, but rockets use the combustion exhaust gases. In outer space there is no atmosphere so turbines and propellers can not work there. This explains why a rocket works in space but a turbine engine or a propeller does not work.
On Earth, air tends to inhibit the exhaust gases getting out of the engine. This reduces the thrust. However, in space since there is no atmosphere, the exhaust gases can exit much easier and faster, thus increasing the thrust. Therefore, the rocket engine actually works better in space than here on Earth.
When a rocket shoots fuel out one end, this propels the rocket forward — no air is required.
In a rocket engine , fuel and a source of oxygen, called an oxidizer, are mixed and exploded in a combustion chamber. The combustion produces hot exhaust which is passed through a nozzle to accelerate the flow and produce thrust.
Turbine engines and propellers use air from the atmosphere as the working fluid, but rockets use the combustion exhaust gases. In outer space there is no atmosphere so turbines and propellers can not work there. This explains why a rocket works in space but a turbine engine or a propeller does not work.
On Earth, air tends to inhibit the exhaust gases getting out of the engine. This reduces the thrust. However, in space since there is no atmosphere, the exhaust gases can exit much easier and faster, thus increasing the thrust. Therefore, the rocket engine actually works better in space than here on Earth.
Most documented Rocket Launch
Video Atlas 5, 551
Sky still black
Eventually Plume gets illuminated, shining sun
Gases forming line
Gases expand more and more as rocket gains altitude
Expanded so much you cannot see.
We are see atmospheric pressure change in real time.
This shows that not only is the rocket not going down, that is just Perspective, but it is gaining altitude as it goes into space/vacuum
Not exploding by hitting the dome.
Gradient of pressure.
Barometric height formula... X, pressure that high. Mt Everest 1/3 pressure sea level.
Video Atlas 5, 551
Sky still black
Eventually Plume gets illuminated, shining sun
Gases forming line
Gases expand more and more as rocket gains altitude
Expanded so much you cannot see.
We are see atmospheric pressure change in real time.
This shows that not only is the rocket not going down, that is just Perspective, but it is gaining altitude as it goes into space/vacuum
Not exploding by hitting the dome.
Gradient of pressure.
Barometric height formula... X, pressure that high. Mt Everest 1/3 pressure sea level.
1) 2:17 can anyone proove that the "Garbage Can" is going faster than 60 to 100mph?
You can't prove it's not.
Yes, As it came back around it was going over 17,000 mph...
2)How Much Acceleration is there in the first 1min of lift off? putting the petal to the metal on my car I can probably get 0-60 in abot 4-5 second on normal slow drive probably need 10-15sec.
9million pounds of thrust and rocket weights over 5 million pounds.
If you work out the math the
3) The Garbage Can Blimp took 5-10 seconds just to clear the tower at about 500 foot high. what is the speed/acceleration there? 0-500 or 1000 feet in 10sec. sounds slower than my car😂
Learn math and figure it out for yourself because you won't accept his answer no matter what it is.
4) When you shoot a gun the bullet goes at about 1500mph+ you don't see the bullet due to the speed(size) of the bullet, but the garbage can blimp rocket is suppose to reach speed of atleat 5000mph - 10,000 mph before reaching outer space and 17500mph to punch through the atmosphere and go to outer space which is about 500 miles high where the ISS Fake Station is suppose to be ????? a)Is this even possible? b)How much accelaration is needed per second to travel 500miles and reach 17500mph? c) can anything on earth withstand those G- Forces.
(a) yes. (b) do the math (c) lean how g-forces work.
5a) How did The garbage can reach 5 or 10,000mph in a distance needed to travel of only 500 miles up and yet still 'be Seen' chugging along, when bullets can't be seen at 1/5 or 1/10 the speed of the supposed garbage can is suppose to be traveling?
by going faster and faster without any wind resistance or friction.
5b) If the "Garbage Can" has to orbit Earth before going to Space, How did it do that when it lost its booster and fuel separaton within first 2 min or 3 min of lift off?
other propulsion source takes very little to increase speed in space and... the slingshot effect of the Earth's gravity. I know that last part is hard for you to understand.
6) provide some details of when? where? and how long since lift off as a point of refrence? is the garbage can reaching speeds of 2500 - 5000 mph. is it still in the atmosphere? If so why is it not ripping apart when reaching the ludicrus speeds that are faster than the best Aero dynamic Jet Fighters?
7) Within about 1:20sec of lift off, The Rocket started to curve How high did it go before curving/falling down?😂
8) about 3:24sec after lift off ( in some of the live videos on youtube) the garbage can is at the horizen a.k.a in the Ocean.
@DFE3 Hi professor some Technical issues/questions of the Rocket Blip and the capsule cartoon.
Rocket first
1) What is it made of? is that giant orange tank copper, steel, aluminum, PVC plastic or what? is it some super duper magical material (like carbon Nano tube)that gives extra strength and makes it extra light.
How much does it weight?
same for boosters?
What is the temprature that is suppose to be of the rocket blimp exhause/fire and why the tower aluminum/metal scafolting doest melt from the rocket flame exhaust?
what is the minimum thrust need to lift 560 000 Liters of Fuel + the weight of the rocket metal tank +booster weight + capsule weight in total weight probably 1 000 000 kg or more.
Show a test (in smaller size that can be scaled up) done on earth as example that the fuel of the rocket Blimp can push forword or upwards of 500000 kg or less/ smaller amount at speeds of 5000mph or more maybe 10000mph. that Garbage can is suppose to reach close to 17000 mph before leaving Earth.
The Capsule
There was news report showing the inside cabin of the capsule to be catapulted into space with a dummy inside (probably a physicist) and electeonics some as computer monitors.
The electronics require a temprature of somewhere between +20⁰c and -20⁰c let make it +40⁰C and -40⁰C any colder or hoter the electronic would freeze or melt and not function. Q1 How does the capsure maintain stable temprature in space when tempratures swing between +400⁰C and -400⁰C? between sunlight and shade such as the dark side of the moon when the capsule orbits it. what kind of magical heat and cold A/C are the using and how much space does it take? (i would like to buy one of these magical instant heaters and coolers😂)
Now does it do that prevent it from freezing or melting at the high temprature suids for the outside of the caplse also( do the solar panes have a blow dryer installed to melt the capsure from freezing😂) and what keeps the solar panes from frezing or melting?
provide some details as to the size of capsule battery size the solar panels are charging, size of the AC unit and fuel tank needed plus minus the interior space needed for the dummy ( physisict) that is already in ther and space thay might not be used for the extra 2 or three crew member that the shuttle is suppose to cary. also include the space that will be needed for oxygen tanks food supply and space suits closet that will be needed for the maned crew.
What precaution have they taken or built into the capsule so that the van allen belt deadly radiation doest destroy the electronics or the dummy (physicist inside😂)