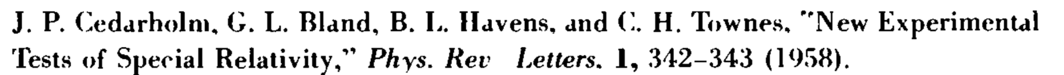So if you think about it, the Foucault pendulum is a kind of rotation meter, it's a way of measuring rotations.
A suitably placed Foucault pendulum can be used to detect the rotation of the earth, or the rotation of the earth around the sun, or in principle you could use a suitably oriented Foucault pendulum to measure the rotation of the solar system around the galaxy.
So this brings up the question, the Foucault pendulum is sensitive to rotation but rotation around what?
There seems to be a lot of speculation in physics and philosophy about that questions. Ernst Mach, 19th-20th century physicist put forward the conjecture that the Foucault pendulum is measuring rotation relative to the universe as a whole.
It makes an interesting connection between a local physics experiment here in this room and the universe as a whole.
The problem is how can this pendulum here somehow know something about the entire universe.
But this remains an unproven conjecture more in the realm of philosophy than physics.
A suitably placed Foucault pendulum can be used to detect the rotation of the earth, or the rotation of the earth around the sun, or in principle you could use a suitably oriented Foucault pendulum to measure the rotation of the solar system around the galaxy.
So this brings up the question, the Foucault pendulum is sensitive to rotation but rotation around what?
There seems to be a lot of speculation in physics and philosophy about that questions. Ernst Mach, 19th-20th century physicist put forward the conjecture that the Foucault pendulum is measuring rotation relative to the universe as a whole.
It makes an interesting connection between a local physics experiment here in this room and the universe as a whole.
The problem is how can this pendulum here somehow know something about the entire universe.
But this remains an unproven conjecture more in the realm of philosophy than physics.
|
Stars
Diurnal Motion – Possibly the First Evidence of Spherical Earth Explains parallax exactly (negative parallax are just statistical uncertainties. Explains precession and stars slowly changing 26,000 year cycle Explains why the 12 zodiac constellations appear when they do each time of year at the equator Outdoor experiment with telescope using notecards for moon and sun Nautical Almanac Polaris only seen North of equator Polaris Altitude and Angle Steller aberration Doppler Effect Proper Motion of Stars Stars Annual Motion |
Planets
Why are all planets Spheres? Explains Epicycles Planetary elliptical orbits predict ours Venus and Mercury Orbits in ecliptic proves earths motion around sun Explains Ecliptic of planets Perihelion of mercury Neptune Moons Orbiting Jupiter |
Alpha Centauri and rotating and moving stars. Two different polestars and two different sets of counterrotating stars above firmament.
Misconception: The position of stars never change.
There are tons of movement the stars do relative to Earth. They all orbit the point above the North Pole, even Polaris, even though it’s very close to it. There’s also stellar parallax that can be measured between summer and winter. There are other stars that change position relatively quickly, within human lifetimes (such as Barnard’s star).
1) Polaris Moving
2) Daily Star Trails
3) Annual Changes
4) Slow Relative Motion
5) Seeing The Large Distances 5000-6000 visible stars.
Stars, planets and bokeh... Lied to we see stars at impossible distances.
Angular size doesn't matter. Luminosity and brightness do
Daily, Annual and Relative Motions... precession and back and forth rocking.
==> All the stars we see in the night sky are relatively close to us in the Galactic sense and traveling around the center of the galaxy with us and you are not going to see much movement.
Misconception: The position of stars never change.
There are tons of movement the stars do relative to Earth. They all orbit the point above the North Pole, even Polaris, even though it’s very close to it. There’s also stellar parallax that can be measured between summer and winter. There are other stars that change position relatively quickly, within human lifetimes (such as Barnard’s star).
1) Polaris Moving
2) Daily Star Trails
3) Annual Changes
4) Slow Relative Motion
5) Seeing The Large Distances 5000-6000 visible stars.
Stars, planets and bokeh... Lied to we see stars at impossible distances.
Angular size doesn't matter. Luminosity and brightness do
Daily, Annual and Relative Motions... precession and back and forth rocking.
==> All the stars we see in the night sky are relatively close to us in the Galactic sense and traveling around the center of the galaxy with us and you are not going to see much movement.
These are the equations witsit needs to use to get his frame dragging effect from a large rotating mass to create Coriolis and Centrifual forces.
Then he needs to model it on a flat earth, and account for the huge mass gravtitational effects upwards.
Relative to What? Cosmic background...
Rotation of Earth
Earth around Sun
Sun Around Galaxy
Precession
Nutation
Rotation
Wobbles (daily and yearly)
Lense Thirring precession
Geodetic Precession (object orbiting central mass).
But if motion of pendulum here influenced by stars out there, how can the stars wobble around the earth...
Then he needs to model it on a flat earth, and account for the huge mass gravtitational effects upwards.
Relative to What? Cosmic background...
Rotation of Earth
Earth around Sun
Sun Around Galaxy
Precession
Nutation
Rotation
Wobbles (daily and yearly)
Lense Thirring precession
Geodetic Precession (object orbiting central mass).
But if motion of pendulum here influenced by stars out there, how can the stars wobble around the earth...
What is a Foucault pendulum eventually rotating around? There is no answer to that question. Moreover, it is not yet clear whether the question makes sense or not.
The most close answer to your question may be found in our motion relative to the Background radiation, found by means of the dipole anisotropy of the CBR. This is the closest thing that there is, to an "absolute reference frame" but it makes sense only for us. Other distant observers in out expanding Universe will have a completely different perception.
As for Mach's principle, let me stress that it is merely a philosophical idea, that may or may not some day lead to a real theory. It is neither correct nor incorrect.
The most close answer to your question may be found in our motion relative to the Background radiation, found by means of the dipole anisotropy of the CBR. This is the closest thing that there is, to an "absolute reference frame" but it makes sense only for us. Other distant observers in out expanding Universe will have a completely different perception.
As for Mach's principle, let me stress that it is merely a philosophical idea, that may or may not some day lead to a real theory. It is neither correct nor incorrect.
The BIG Problem with invoking anitquated quotes to prove a stationary Earth in 2022
The Big Problem is the Well Validated Big Bang Cosmology
I-nye-so-tropy
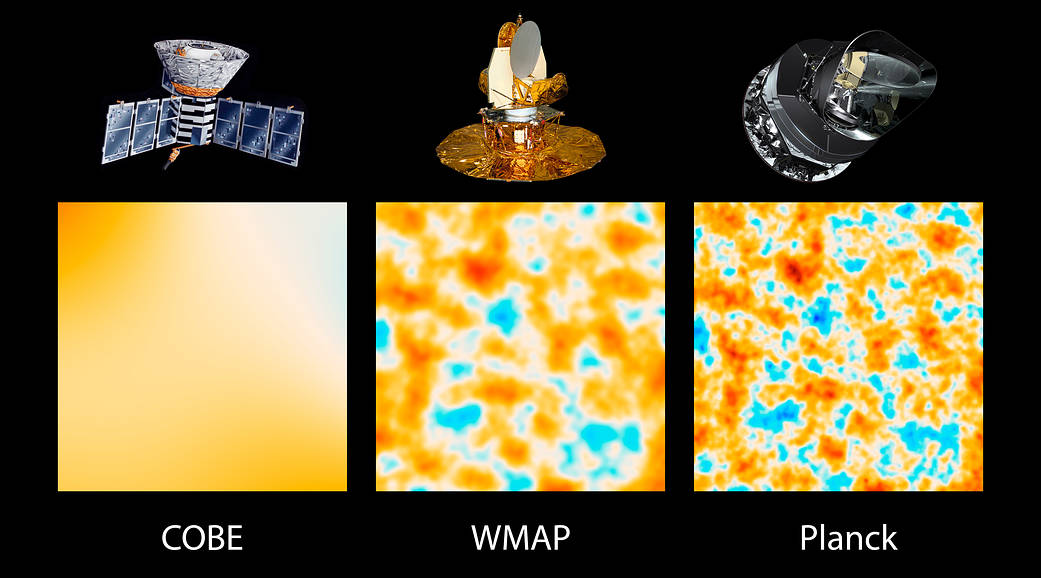
1989, is NASA's Cosmic Background Explorer, or COBE (left panel). Two of COBE's principal scientists earned the Nobel Prize in Physics in 2006 for the mission's evidence supporting the big bang theory, and for its demonstration that tiny variations in the ancient light reveal information about the state of the universe.
Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe, or WMAP (middle panel). This mission, launched in 2001, found strong evidence for inflation, the very early epoch in our universe when it expanded dramatically in size, and measured basic traits of our universe better than ever before.
The most advanced satellite yet of this type is Planck, a European Space Agency mission with significant NASA contributions. Planck, launched in 2009, images the sky with more than 2.5 times greater resolution than WMAP,
The Big Problem is the Well Validated Big Bang Cosmology
I-nye-so-tropy
1989, is NASA's Cosmic Background Explorer, or COBE (left panel). Two of COBE's principal scientists earned the Nobel Prize in Physics in 2006 for the mission's evidence supporting the big bang theory, and for its demonstration that tiny variations in the ancient light reveal information about the state of the universe.
Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe, or WMAP (middle panel). This mission, launched in 2001, found strong evidence for inflation, the very early epoch in our universe when it expanded dramatically in size, and measured basic traits of our universe better than ever before.
The most advanced satellite yet of this type is Planck, a European Space Agency mission with significant NASA contributions. Planck, launched in 2009, images the sky with more than 2.5 times greater resolution than WMAP,
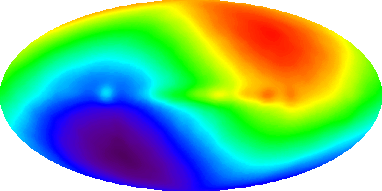
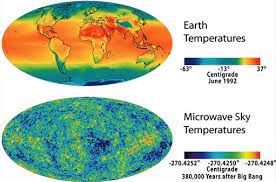
There are experimental evidences of absolute motion of the Earth around the Sun. There is a dipole anisotropy in fine measures of the Background Radiation temperature that is known from the analysis of the COBE satellite measures, in the early 90s.
In order to make the adequate corrections, so that the Cosmic Background Radiation "seems" isotropic, the absolute velocity of the Local Group against the Cosmic Background Radiation must be accounted for, but that correction depends on the month of the year, because a small part of the correction comes from the orbital speed of the Earth around the barycentre of the Solar System (among other terms).
That small part of the corrections needed is exactly what you would expect if you assumed that is the Earth who is going around the Sun, and not vice versa.
(the cosmic background dipole anisotropy, image from map.gsfc.nasa.gov)
In order to make the adequate corrections, so that the Cosmic Background Radiation "seems" isotropic, the absolute velocity of the Local Group against the Cosmic Background Radiation must be accounted for, but that correction depends on the month of the year, because a small part of the correction comes from the orbital speed of the Earth around the barycentre of the Solar System (among other terms).
That small part of the corrections needed is exactly what you would expect if you assumed that is the Earth who is going around the Sun, and not vice versa.
(the cosmic background dipole anisotropy, image from map.gsfc.nasa.gov)

Here is an extract from the abstract of the quoted paper:
https://arxiv.org/pdf/astro-ph/9312056.pdf
We present a determination of the cosmic microwave background dipole amplitude and direction from the COBE Differential Microwave Radiometers (DMR) first year of data (...) The implied velocity of the Local Group with respect to the CMB rest frame is 𝑣𝐿𝐺=627±22𝑘𝑚𝑠−1 toward (...). DMR has also mapped the dipole anisotropy resulting from the Earth's orbital motion about the Solar System barycenter, yielding a measurement of the monopole CMB temperature (...) 𝑇0=2.75±0.05𝐾
This doesn't mean however, that there is an absolute reference frame in the Universe. Other comoving observers will detect another dipole anisotropy. The Last Scattering Surface, as well as the cosmological horizons are different for different comoving observers. But nevertheless it proves that it is the Earth that moves around the Sun, and not vice versa. Since the 90s this is no more a philosophical issue: WE are moving certainly, absolutely, surely and gloriously, around the Sun.
https://arxiv.org/pdf/astro-ph/9312056.pdf
We present a determination of the cosmic microwave background dipole amplitude and direction from the COBE Differential Microwave Radiometers (DMR) first year of data (...) The implied velocity of the Local Group with respect to the CMB rest frame is 𝑣𝐿𝐺=627±22𝑘𝑚𝑠−1 toward (...). DMR has also mapped the dipole anisotropy resulting from the Earth's orbital motion about the Solar System barycenter, yielding a measurement of the monopole CMB temperature (...) 𝑇0=2.75±0.05𝐾
This doesn't mean however, that there is an absolute reference frame in the Universe. Other comoving observers will detect another dipole anisotropy. The Last Scattering Surface, as well as the cosmological horizons are different for different comoving observers. But nevertheless it proves that it is the Earth that moves around the Sun, and not vice versa. Since the 90s this is no more a philosophical issue: WE are moving certainly, absolutely, surely and gloriously, around the Sun.

Planets - Show me the Orbits!
**The earth is not stationary & (and it sure isn't flat)!**
Flat-Earthers claim that Earth is stationary. In reality, from observing the planets’ motion, the most plausible explanation is that all planets, including Earth, are in motion around the Sun.
Planets appear to move near the ecliptic —the line that marks the annual path of the Sun against background stars. From these motions, it is obvious that Venus and Mercury are in motion around the Sun. And the motion of the other planets can only be explained if Earth is in motion around the Sun. Otherwise you end up with the ole' epicycle problem of the Ptolemaic geocentric model. A problem that the heliocentric model corrected and simplified , but sadly a problem the flat earth model makes even worse because at least the Geocentric model had the earth as a sphere!
Ancient Greeks called these lights planētes asteres, "wandering stars" or simply planētai, "wanderers"), from which today's word "planet" was derived.
This is mars photographed once a week over a period of months. Rather than traveling in a straight line across the background of the stars, it occasionally changes direction and loops back on itself. It is very hard to explain these retrograde loops if the earth is at the center of the universe.
Took over 2000 years to work this retrograde motion, key is understanding the Sun is at the center of the solar system, not the earth.
**The earth is not stationary & (and it sure isn't flat)!**
Flat-Earthers claim that Earth is stationary. In reality, from observing the planets’ motion, the most plausible explanation is that all planets, including Earth, are in motion around the Sun.
Planets appear to move near the ecliptic —the line that marks the annual path of the Sun against background stars. From these motions, it is obvious that Venus and Mercury are in motion around the Sun. And the motion of the other planets can only be explained if Earth is in motion around the Sun. Otherwise you end up with the ole' epicycle problem of the Ptolemaic geocentric model. A problem that the heliocentric model corrected and simplified , but sadly a problem the flat earth model makes even worse because at least the Geocentric model had the earth as a sphere!
Ancient Greeks called these lights planētes asteres, "wandering stars" or simply planētai, "wanderers"), from which today's word "planet" was derived.
This is mars photographed once a week over a period of months. Rather than traveling in a straight line across the background of the stars, it occasionally changes direction and loops back on itself. It is very hard to explain these retrograde loops if the earth is at the center of the universe.
Took over 2000 years to work this retrograde motion, key is understanding the Sun is at the center of the solar system, not the earth.
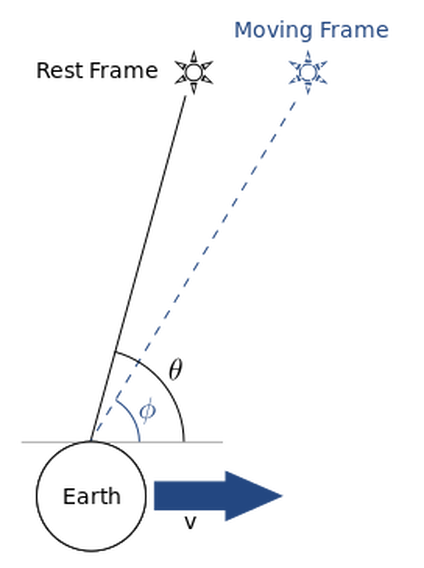
You're all familiar with this effect: suppose that you're standing in the rain, and there's no wind. Since the rain will fall vertically, you have to hold your umbrella straight up. But now start running. What happens? From your point of view, the rain will no longer fall vertically: you have to tilt your umbrella forward to keep your head dry. A similar phenomenon happens with light: the direction in which you see a beam of light depends on your velocity. This effect is called aberration.
For instance, suppose you have two stars, separated by an angle 𝜃 in a rest frame. If an observer is moving towards the star on the horizontal axis, then he will see the second star at an angle 𝜑, instead of 𝜃. If the velocity of the observer changes, then the angle 𝜑 changes, and the star will appear to 'wobble' with respect to stars at different positions.
The orbital velocity 𝑣≈30km/s of the Earth around the Sun causes an annual aberration: over the period of a year, every star and galaxy will appear to wobble on an ellipse, with a maximum displacement of 𝑣/𝑐≈20.5″ around their mean position, regardless of their distance to the Earth (unlike parallax, which does depend on distance). It was first observed by James Bradley in 1725, and is direct proof that the Earth orbits the Sun.
But there's another, much smaller aberration: a diurnal aberration, caused by the rotation of the Earth around its axis. The effect is greatest for an observer on the equator, who has an equatorial speed of 𝑣=0.465km/s, while an observer on the poles will see no effect. For an observer on the equator, the position of every star wobbles on a daily basis, with a maximum displacement of 𝑣/𝑐≈0.32″. It's an incredibly small effect, but it is measurable, and it has to be taken into account when doing high-precision astrometry. Moreover, it proves that the Earth does rotate.
Another proof that the Earth rotates, although it can only be measured with modern techniques: aberration.
For instance, suppose you have two stars, separated by an angle 𝜃 in a rest frame. If an observer is moving towards the star on the horizontal axis, then he will see the second star at an angle 𝜑, instead of 𝜃. If the velocity of the observer changes, then the angle 𝜑 changes, and the star will appear to 'wobble' with respect to stars at different positions.
The orbital velocity 𝑣≈30km/s of the Earth around the Sun causes an annual aberration: over the period of a year, every star and galaxy will appear to wobble on an ellipse, with a maximum displacement of 𝑣/𝑐≈20.5″ around their mean position, regardless of their distance to the Earth (unlike parallax, which does depend on distance). It was first observed by James Bradley in 1725, and is direct proof that the Earth orbits the Sun.
But there's another, much smaller aberration: a diurnal aberration, caused by the rotation of the Earth around its axis. The effect is greatest for an observer on the equator, who has an equatorial speed of 𝑣=0.465km/s, while an observer on the poles will see no effect. For an observer on the equator, the position of every star wobbles on a daily basis, with a maximum displacement of 𝑣/𝑐≈0.32″. It's an incredibly small effect, but it is measurable, and it has to be taken into account when doing high-precision astrometry. Moreover, it proves that the Earth does rotate.
Another proof that the Earth rotates, although it can only be measured with modern techniques: aberration.

Stellar motion would imply we're in the place where the Big Bang occurred while everything else is speeding away from us. I can see how this would be a worthwile explanation for a creationist, but it doesn't really make much sense building just on physics.
Doppler Effect has the same issue - it assumes that every star we can see moves in a speed proportional to distance with respect to us. That's extremely Sun-centric, and doesn't really work if you accept that e.g. stars in our galaxy orbit around its center, including us.
Gravitation of course does have effect on wavelength, but it's by far not enough for common stars, much less planets. And of course, the effect is only at work when you're in the gravitational well - this would imply that the Sun is again at the center of everything, with everything else orbitting around it.
Photon interaction - never been observed, doesn't really play well with accepted theories of electro-magnetism and photons. With the exception of - the expansion of space itself. Yes, photons are losing energy, that's why they're red-shifted. Even though there is a certain preference for photons to fill in similar states, this mostly manifests as a tendency for self-collimation. Interacting photons would not explain why the red-shift is correlated with distance either.
The others work in a similar fashion. Slowing of light would have huge effects on every interaction in the universe - which would mean that even things like water wouldn't be stable over time, they would change their behaviour rather a lot. Combined with the proposed age of ~6000 years for the universe, with humans from the very beginning, this is just absurd. The assumptions made by theory of relativity make this even more crazy - in relativity, speed of light is basically the maximum speed of propagation of information. So this hinges on older models of the speed of light, independent of the space-time itself.
Galaxies spiraling towards the Earth was already handled in the Gravitational red-shift explanation and the Doppler effect.
All in all, you can see why a creationist-proponent would like those theories. They mostly work on the basis that we are at the center of everything, and everything else revolves around us. It's the good old Earth-centric solar system model again, just dressed in the universe this time.
The problem is, addressing every single hypothesis put forward by people lacking in basic science practice and knowledge is fighting windmills. You can always imagine sillier and sillier explanations, and when people finally get tired of responding, you'll just say "See? The scientists have no explanation for that!" It's an uphill battle, and somewhat pointless, really.
Don't forget that when you propose an alternative theory/hypothesis, you need to explain everything the old theory did. If we find out that photons travel at lower or higher speeds than the speed of light, it might put relativity out of the question, but we'll still have to find out why it works almost all the time we've checked. It's possible to "overthrow" a well established theory, but most often, you're only adding to what's already there. For example, Newton's law of gravity is wrong, but it's not thrown out outright - it's simply explained differently, and broadened to explain new observations. Most of the time, it works well enough. If it starts contradicting your observations (like the famous precession of Mercury issue), you start refining - in this case, Einstein pretty much redefined the whole universe. But it didn't make the old theory wrong outright - just incomplete. Creationist hypothesis tend to ignore this completely - they focus on one pet theory, and ignore the other explanations that need to be done to maintain a consistent model.
Doppler Effect has the same issue - it assumes that every star we can see moves in a speed proportional to distance with respect to us. That's extremely Sun-centric, and doesn't really work if you accept that e.g. stars in our galaxy orbit around its center, including us.
Gravitation of course does have effect on wavelength, but it's by far not enough for common stars, much less planets. And of course, the effect is only at work when you're in the gravitational well - this would imply that the Sun is again at the center of everything, with everything else orbitting around it.
Photon interaction - never been observed, doesn't really play well with accepted theories of electro-magnetism and photons. With the exception of - the expansion of space itself. Yes, photons are losing energy, that's why they're red-shifted. Even though there is a certain preference for photons to fill in similar states, this mostly manifests as a tendency for self-collimation. Interacting photons would not explain why the red-shift is correlated with distance either.
The others work in a similar fashion. Slowing of light would have huge effects on every interaction in the universe - which would mean that even things like water wouldn't be stable over time, they would change their behaviour rather a lot. Combined with the proposed age of ~6000 years for the universe, with humans from the very beginning, this is just absurd. The assumptions made by theory of relativity make this even more crazy - in relativity, speed of light is basically the maximum speed of propagation of information. So this hinges on older models of the speed of light, independent of the space-time itself.
Galaxies spiraling towards the Earth was already handled in the Gravitational red-shift explanation and the Doppler effect.
All in all, you can see why a creationist-proponent would like those theories. They mostly work on the basis that we are at the center of everything, and everything else revolves around us. It's the good old Earth-centric solar system model again, just dressed in the universe this time.
The problem is, addressing every single hypothesis put forward by people lacking in basic science practice and knowledge is fighting windmills. You can always imagine sillier and sillier explanations, and when people finally get tired of responding, you'll just say "See? The scientists have no explanation for that!" It's an uphill battle, and somewhat pointless, really.
Don't forget that when you propose an alternative theory/hypothesis, you need to explain everything the old theory did. If we find out that photons travel at lower or higher speeds than the speed of light, it might put relativity out of the question, but we'll still have to find out why it works almost all the time we've checked. It's possible to "overthrow" a well established theory, but most often, you're only adding to what's already there. For example, Newton's law of gravity is wrong, but it's not thrown out outright - it's simply explained differently, and broadened to explain new observations. Most of the time, it works well enough. If it starts contradicting your observations (like the famous precession of Mercury issue), you start refining - in this case, Einstein pretty much redefined the whole universe. But it didn't make the old theory wrong outright - just incomplete. Creationist hypothesis tend to ignore this completely - they focus on one pet theory, and ignore the other explanations that need to be done to maintain a consistent model.
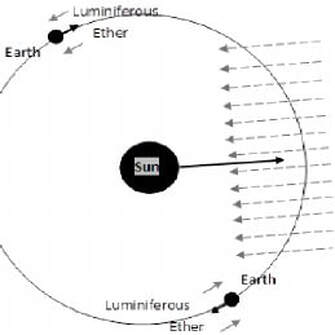
Michelson-Morley’s 1887 experiment falsified the Aether hypothesis. Flat earthers reject this conclusion and claim the experiment “proved the earth is stationary”. They often misquote Bernard Jaffe’s writings from 1960 to support this false claim.
Sir George Stokes proposed that the Aether is at rest in relation to the surface of the earth
From the 1887 paper by Michelson and Morley, If you were to ignore all other evidence of rotation like opposite rotating celestial poles, stellar parallax, the precession of the equinoxes, Coriolis, Eötvös, etc. one could propose that the earth is stationary. However, in 1925, Michelson, Gale, and Pearson published another experiment that measured the difference in time taken for light to travel in opposite directions around a large rectangle.
Flat earthers interpret this as the aether swirling around the surface of the earth.
If the earth and aether are stationary according to Michelson-Morley, then the aether cannot simultaneously be swirling around according to Michelson-Gale. You can’t have both.
https://www.universetoday.com/22912/more-evidence-earth-is-not-center-of-universe/
From the 1887 paper by Michelson and Morley, If you were to ignore all other evidence of rotation like opposite rotating celestial poles, stellar parallax, the precession of the equinoxes, Coriolis, Eötvös, etc. one could propose that the earth is stationary. However, in 1925, Michelson, Gale, and Pearson published another experiment that measured the difference in time taken for light to travel in opposite directions around a large rectangle.
Flat earthers interpret this as the aether swirling around the surface of the earth.
If the earth and aether are stationary according to Michelson-Morley, then the aether cannot simultaneously be swirling around according to Michelson-Gale. You can’t have both.
https://www.universetoday.com/22912/more-evidence-earth-is-not-center-of-universe/
Of course Witsit Knows this is a problem, because he invokes the moving Aether to explain rotational effects on earth. So he has to find ways to bring in a fringe shift that dozens of studies show doesn't exist... Well except for one, the Infamous
Airforce Study 1986
Airforce Study 1986
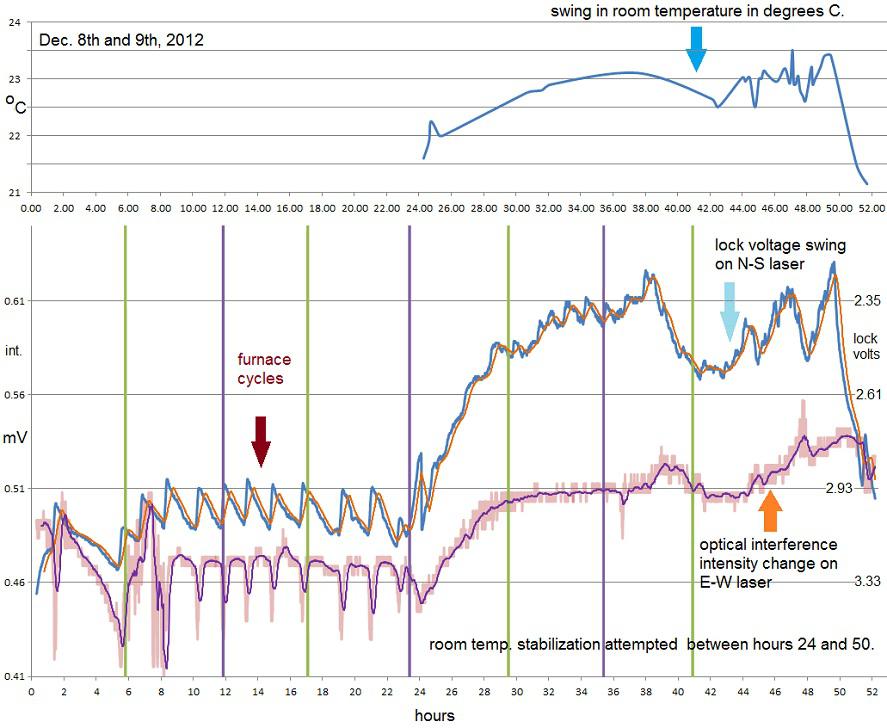
But in 2012 Doug Marett actually repeated the experiment, and what he found is fascinating.
Over the course of 18 months Marett recreated the Silvertooth experiment, and confirmed the result. There was an apparent shift in wavelength that varied with the orientation of Earth, and it did seem to show an apparent motion of Earth in agreement with Silvertooth's intial findings. But looking at the data more carefully, Marett also found that there was a lot of fluctuation in the data.
If Silvertooth was right, the wavelength variations should follow sidereal time, not solar time. Marett found there was so much noise in the data, the variation in wavelengths could be made to agree with either sidereal or solar time. Digging into things more closely, he saw a correlation between the observed wavelength shift and small fluctuations in the temperature of the room. The change in temperature was shifting the alignment of the experiment laser, causing the apparent shift Silvertooth saw. Marett also found that the calculated motion of the Earth only worked because Silvertooth assumed the data measured an actual wavelength shift. Silvertooth's results were real, but his conclusions were wrong.
Over the course of 18 months Marett recreated the Silvertooth experiment, and confirmed the result. There was an apparent shift in wavelength that varied with the orientation of Earth, and it did seem to show an apparent motion of Earth in agreement with Silvertooth's intial findings. But looking at the data more carefully, Marett also found that there was a lot of fluctuation in the data.
If Silvertooth was right, the wavelength variations should follow sidereal time, not solar time. Marett found there was so much noise in the data, the variation in wavelengths could be made to agree with either sidereal or solar time. Digging into things more closely, he saw a correlation between the observed wavelength shift and small fluctuations in the temperature of the room. The change in temperature was shifting the alignment of the experiment laser, causing the apparent shift Silvertooth saw. Marett also found that the calculated motion of the Earth only worked because Silvertooth assumed the data measured an actual wavelength shift. Silvertooth's results were real, but his conclusions were wrong.
Aether was the hypothetical material that fills the region of space. It was assumed to be the medium that allows light and gravity to propagate in space. Throughout the late 1800s and early 1900s, some experiments were carried out to prove if the aether exists.
Flat-Earthers (and geocentrists alike) often use the results of these experiments to support their case that the Earth is stationary. But they are wrong. These experiments were conducted to prove if the Aether theory, or if one of its competing hypotheses —like the Special Relativity— better explains reality.
In 1871, George Airy attempted to measure the drag of light that would change the stellar aberration of light by using a water-filled telescope, instead of an air-filled one. His observation did not indicate the change exists and does not support the Aether drag hypothesis, hence the popular name “Airy’s failure.” It does not support a flat & stationary Earth as the underlying phenomenon —the annual stellar aberration— can only occur if the Earth is in motion around the Sun.
The Michelson-Morley experiment in 1887 proved that if the Earth is in motion, then Aether could not exist. This experiment alone cannot confirm if the Earth is or is not in motion, but that does not stop flat-Earthers. The fact that the Earth is in motion had to be concluded from other observations.
Georges Sagnac in 1913 conducted an experiment where he rotated his interferometer. He concluded the Aether exists, but only because he was unaware of what we call now the Sagnac effect. This effect is used today in optical gyroscopes, and cannot possibly be utilized had the Aether theory is correct.
The Michelson–Gale–Pearson experiment (1926) was a very large interferometer designed to detect Earth’s rotation by measuring the resulting Sagnac effect. The experiment was successful and confirmed the angular velocity due to Earth’s rotation.
Flat-Earthers (and geocentrists alike) often use the results of these experiments to support their case that the Earth is stationary. But they are wrong. These experiments were conducted to prove if the Aether theory, or if one of its competing hypotheses —like the Special Relativity— better explains reality.
In 1871, George Airy attempted to measure the drag of light that would change the stellar aberration of light by using a water-filled telescope, instead of an air-filled one. His observation did not indicate the change exists and does not support the Aether drag hypothesis, hence the popular name “Airy’s failure.” It does not support a flat & stationary Earth as the underlying phenomenon —the annual stellar aberration— can only occur if the Earth is in motion around the Sun.
The Michelson-Morley experiment in 1887 proved that if the Earth is in motion, then Aether could not exist. This experiment alone cannot confirm if the Earth is or is not in motion, but that does not stop flat-Earthers. The fact that the Earth is in motion had to be concluded from other observations.
Georges Sagnac in 1913 conducted an experiment where he rotated his interferometer. He concluded the Aether exists, but only because he was unaware of what we call now the Sagnac effect. This effect is used today in optical gyroscopes, and cannot possibly be utilized had the Aether theory is correct.
The Michelson–Gale–Pearson experiment (1926) was a very large interferometer designed to detect Earth’s rotation by measuring the resulting Sagnac effect. The experiment was successful and confirmed the angular velocity due to Earth’s rotation.
Flat earthers misrepresent Airy's experiment and the implications. What Airy, and Michelson-Morley, showed was there is no aether that we are moving through.
Michelson-Gale-Pearson, Sagnac, Compton, et al. proved Earth's motion around the Sun and Rotation about an axis. The observed annual stellar aberration, or apparent motion of celestial objects about their true positions, is dependent on the velocity of the observer which also proves the Earth is moving. What finally accounted for all observations is Einstein's Relativity.
Michelson-Gale-Pearson, Sagnac, Compton, et al. proved Earth's motion around the Sun and Rotation about an axis. The observed annual stellar aberration, or apparent motion of celestial objects about their true positions, is dependent on the velocity of the observer which also proves the Earth is moving. What finally accounted for all observations is Einstein's Relativity.
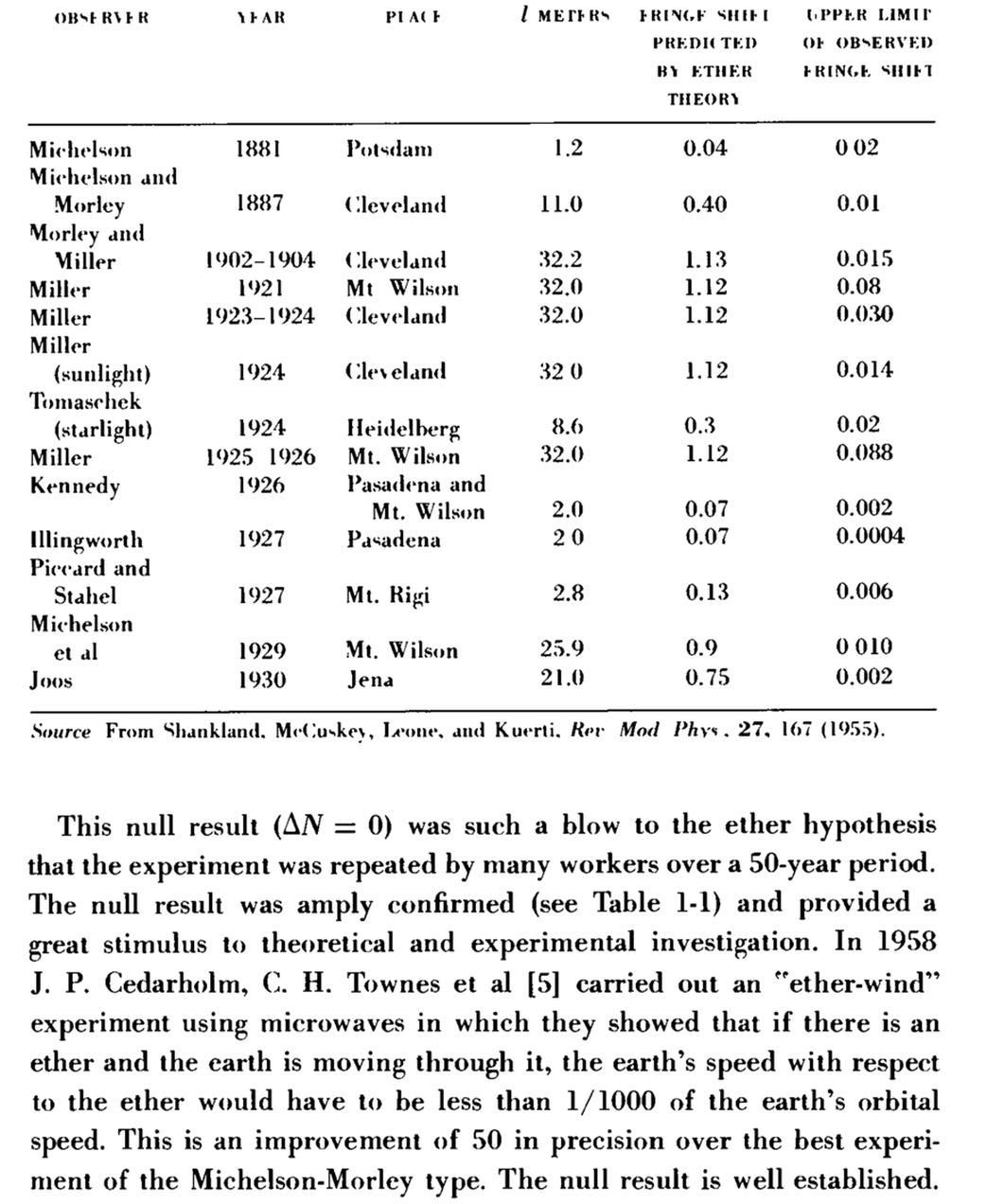
Michelson's terse description of the experiment: "The interpretation of these results is that there is no displacement of the interference bands. ... The result of the hypothesis of a stationary ether is thus shown to be incorrect." (A. A. Michelson, Am. J. Sci, 122, 120 (1881))
Further, with respect to Einstein saying Earth's orbit around the Sun can't be detected, Witsit is cherry picking from that quote as well and taking it out of context. The following is the actual quote along with the preceding paragraph to make the context clear: "Then I myself wanted to verify the flow of the ether with respect to the Earth, in other words, the motion of the Earth. When I first thought about this problem, I did not doubt the existence of the ether or the motion of the Earth through it. I thought of the following experiment using two thermocouples: Set up mirrors so that the light from a single source is to be reflected in two different directions, one parallel to the motion of the Earth and the other antiparallel. If we assume that there is an energy difference between the two reflected beams, we can measure the difference in the generated heat using two thermocouples. Although the idea of this experiment is very similar to that of Michelson, I did not put this experiment to the test. While I was thinking of this problem in my student years, I came to know the strange result of Michelson's experiment. Soon I came to the conclusion that our idea about the motion of the Earth with respect to the ether is incorrect, if we admit Michelson's null result as a fact. This was the first path which led me to the special theory of relativity. Since then I have come to believe that the motion of the Earth cannot be detected by any optical experiment, though the Earth is revolving around the Sun." Witsit is omitting the last part where Einstein acknowledges that Earth is revolving around the Sun. Also, from these two paragraphs, the context is more clear. Einstein initially thought the ether existed and Earth is moving through it. But since Michelson's experiment to detect Earth's motion through the ether failed, Einstein felt that no optical experiment can detect it because light needs ether as a medium for propagation, but that propagation can't be detected. However, later on Einstein realized that the ether doesn't exist and this led to the formulation of his Special Theory of Relativity.
In 1881, Albert A. Michelson experimented to prove the existence of aether. Aether was a hypothesized material that fills the region of the universe. Scientists knew light is a form of a wave, and because all other waves require a medium to propagate, they formulated the aether hypothesis, in which light can propagate. However, Michelson’s attempt produced a null result. Michelson concluded that the hypothesis of a stationary aether is erroneous.
Ether is a frame, in which an observer measures the speed of light to be exactly c. If Galilean transformations really applied to light, then there would be one and only one on which the speed of light is exactly c. That is there is a unique inertial system in which the so called ether is at rest. Only way Galilean transformations and Maxwells work is if there is a unique and privileged frame of reference (the "ether" frame) in which Maxwell's equations are valid and in which light is propagated at a speed c.
Ether is a frame, in which an observer measures the speed of light to be exactly c. If Galilean transformations really applied to light, then there would be one and only one on which the speed of light is exactly c. That is there is a unique inertial system in which the so called ether is at rest. Only way Galilean transformations and Maxwells work is if there is a unique and privileged frame of reference (the "ether" frame) in which Maxwell's equations are valid and in which light is propagated at a speed c.
1. Stationary Ether, no contraction: what was originally thought as the medium or reference frame from which light propagated.
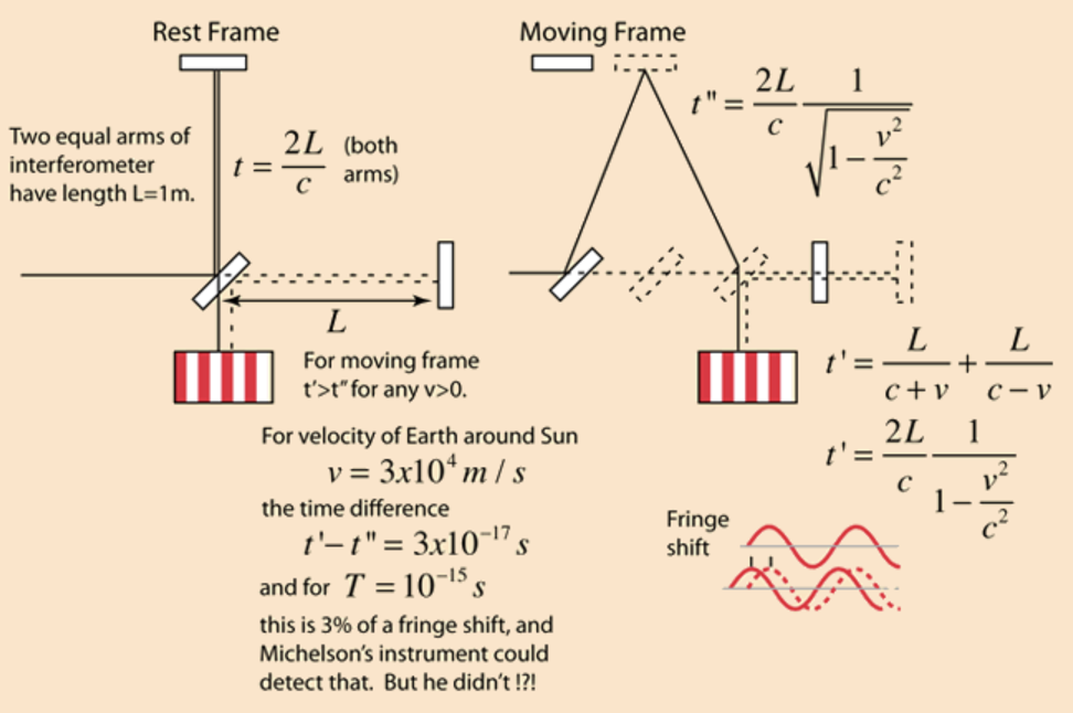
The experimental results showed no shift in the fringe patterns. The only possible conclusion is the earth is traveling with a speed v=0 relative to the ether, to which Michelson himself said was preposterous.
**Should be a shift in the fringe pattern. ΔN = .4 if there is a stationary ether (v/c = 10^-4 based on earth's orbital velocity of 30,000 m/s and light going 3x10^8 m/s.
Another possibility is to conclude the speed of light is the same in all directions in every inertial system**. For this fact would lead to ΔN = 0 in the equal arm experiment, the "downstream/upstream" and cross stream speeds both being c, rather than |c + v| or |c - v|. However such a conclusion being incompatible with Galilean (velocity) transformations, seemed to be too drastic philosophy at the time. If the measured speed of light did not depend on the motion of the observer, all inertial systems would be equivalent for a propagation of light and there would be no experimental evidence to indicate the existence of a unique inertial system, that is, the ether. Therefore to "save the ether" and still explain the Michelson-Morley result, scientists suggested alternative hypotheses which fell under two broad categories.
**Note: Cherenkov (Cher -ain - koff) radiation is not faster Than the speed of light in a vacuum.
J.P. Cedarholm, C.H. Townes carried out an "ether-wind" experiment using microwaves in which they showed an improvement of 50 in precision over the best previous MM type. The null result is well established.
The experimental results showed no shift in the fringe patterns. The only possible conclusion is the earth is traveling with a speed v=0 relative to the ether, to which Michelson himself said was preposterous.
**Should be a shift in the fringe pattern. ΔN = .4 if there is a stationary ether (v/c = 10^-4 based on earth's orbital velocity of 30,000 m/s and light going 3x10^8 m/s.
Another possibility is to conclude the speed of light is the same in all directions in every inertial system**. For this fact would lead to ΔN = 0 in the equal arm experiment, the "downstream/upstream" and cross stream speeds both being c, rather than |c + v| or |c - v|. However such a conclusion being incompatible with Galilean (velocity) transformations, seemed to be too drastic philosophy at the time. If the measured speed of light did not depend on the motion of the observer, all inertial systems would be equivalent for a propagation of light and there would be no experimental evidence to indicate the existence of a unique inertial system, that is, the ether. Therefore to "save the ether" and still explain the Michelson-Morley result, scientists suggested alternative hypotheses which fell under two broad categories.
**Note: Cherenkov (Cher -ain - koff) radiation is not faster Than the speed of light in a vacuum.
J.P. Cedarholm, C.H. Townes carried out an "ether-wind" experiment using microwaves in which they showed an improvement of 50 in precision over the best previous MM type. The null result is well established.
2. Stationary Ether, Lorenz contraction: All bodies contracted relative to a stationary ether by a factor of 1/sqrt(1-v^2/c^2). Interferometer of differing lengths should show a shift in fringes but doesn't.
3. Ether Drag: Ether attached to appreciable bodies. Another attempt to retain the notion of a preferred ether frame. This hypothesis assumed that the ether frame was attached to all bodies of finite mass, that is, dragged along with such bodies. The assumption of a local ether would automatically give a null result in the Michelson-Morley experiment. It's attraction lay in the fact that it did not require modifications of classical mechanics or electromagnetism.
However there were two well established effects which contradicted the ether drag hypothesis: stellar aberration and the Fizeau convection coefficient.
However there were two well established effects which contradicted the ether drag hypothesis: stellar aberration and the Fizeau convection coefficient.
http://curious.astro.cornell.edu/physics/41-our-solar-system/the-earth/orbit/88-is-there-a-proof-that-earth-moves-intermediate
Stellar Aberration and Parallax
How do we know that Earth and other planets go around the Sun, and not the opposite?
The ancient astronomer Aristarchus thought that Earth goes around the Sun since he discovered that the Sun is much bigger than Earth. Copernicus (who is usually credited with the idea that planets go around the Sun) thought that Solar system centered on the Sun is more logical and beautiful, but had no definite proof. Kepler discovered that laws governing of orbits become much more simple if the Sun is in their center. Newton has shown that this is caused by the universal law of gravity. If gravity works, Earth and other planets have to go around the Sun, because it is much heavier.
There was no straightforward demonstration of Earth's motion until 1725 when James Bradley discovered stellar aberration. This is (apparent) yearly change in positions of all stars in the sky due to Earth's own motion. Aberration arises due to adding up of the speed of light coming from the star and Earth's own speed. This is a very complex phenomenon and its description requires some math.
Another, much simpler, consequence of Earth's motion is stellar parallax. If Earth changes its position relative to the stars, then the stars should appear to change position in the course of the year.
A common experiment illustrating parallax is just looking at a close object (a finger, a pencil etc) with one eye at the time. When you switch from one to the other eye, the object will appear to move against the background. Closer the object is to your eyes, more pronounced the effect is.
Parallax should not be confused with aberration: parallax arises from the change of Earth's position and depends on the distance to the star, while aberration is caused by Earth's great speed and does not depend on how far the star is.
Parallax of a star was first measured by Bessel in 1838. It was not measured before because this change of star's apparent position is very small (the stars are very far from us). This was a very important discovery because Aristotle himself mentioned the lack of observable stellar parallax as the proof that the Earth is not moving (he didn't have a telescope and didn't know that the stars are so distant).
A third discovery demonstrating Earth's motion was that of Doppler effect. The wavelength of the light that we receive from objects moving relative to us becomes a little shorter (i.e. bluer) when we approach the source and becomes longer (i.e. redder) when we move away from the source. When Earth moves toward a star, the star will appear slightly bluer (only high-tech instruments can measure this) while it will appear redder when Earth is on the other side of the orbit and moves in the opposite direction. This effect demonstrates that Earth has a velocity relative to the stars, similar to aberration.
All of these phenomena demonstrate Earth's motion relative to other objects. It is important to note that according to the theory of relativity, we can always move to a reference frame in which the Earth is not moving--i.e., its "inertial" reference frame. So it is technically possible to define a reference frame in which the Earth does not move, while the Sun, planets, and stars orbit around the Earth, but making this reference frame consistent with our observations of Doppler shift and parallaxes would be very complicated. It is much simpler to explain our observations in a reference frame where the Earth does move, and Occam's razor directs us, as scientists, to use the simplest explanation whenever possible.
Stellar Aberration and Parallax
How do we know that Earth and other planets go around the Sun, and not the opposite?
The ancient astronomer Aristarchus thought that Earth goes around the Sun since he discovered that the Sun is much bigger than Earth. Copernicus (who is usually credited with the idea that planets go around the Sun) thought that Solar system centered on the Sun is more logical and beautiful, but had no definite proof. Kepler discovered that laws governing of orbits become much more simple if the Sun is in their center. Newton has shown that this is caused by the universal law of gravity. If gravity works, Earth and other planets have to go around the Sun, because it is much heavier.
There was no straightforward demonstration of Earth's motion until 1725 when James Bradley discovered stellar aberration. This is (apparent) yearly change in positions of all stars in the sky due to Earth's own motion. Aberration arises due to adding up of the speed of light coming from the star and Earth's own speed. This is a very complex phenomenon and its description requires some math.
Another, much simpler, consequence of Earth's motion is stellar parallax. If Earth changes its position relative to the stars, then the stars should appear to change position in the course of the year.
A common experiment illustrating parallax is just looking at a close object (a finger, a pencil etc) with one eye at the time. When you switch from one to the other eye, the object will appear to move against the background. Closer the object is to your eyes, more pronounced the effect is.
Parallax should not be confused with aberration: parallax arises from the change of Earth's position and depends on the distance to the star, while aberration is caused by Earth's great speed and does not depend on how far the star is.
Parallax of a star was first measured by Bessel in 1838. It was not measured before because this change of star's apparent position is very small (the stars are very far from us). This was a very important discovery because Aristotle himself mentioned the lack of observable stellar parallax as the proof that the Earth is not moving (he didn't have a telescope and didn't know that the stars are so distant).
A third discovery demonstrating Earth's motion was that of Doppler effect. The wavelength of the light that we receive from objects moving relative to us becomes a little shorter (i.e. bluer) when we approach the source and becomes longer (i.e. redder) when we move away from the source. When Earth moves toward a star, the star will appear slightly bluer (only high-tech instruments can measure this) while it will appear redder when Earth is on the other side of the orbit and moves in the opposite direction. This effect demonstrates that Earth has a velocity relative to the stars, similar to aberration.
All of these phenomena demonstrate Earth's motion relative to other objects. It is important to note that according to the theory of relativity, we can always move to a reference frame in which the Earth is not moving--i.e., its "inertial" reference frame. So it is technically possible to define a reference frame in which the Earth does not move, while the Sun, planets, and stars orbit around the Earth, but making this reference frame consistent with our observations of Doppler shift and parallaxes would be very complicated. It is much simpler to explain our observations in a reference frame where the Earth does move, and Occam's razor directs us, as scientists, to use the simplest explanation whenever possible.
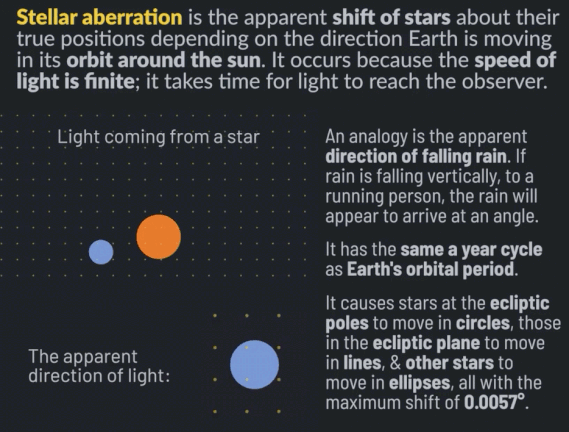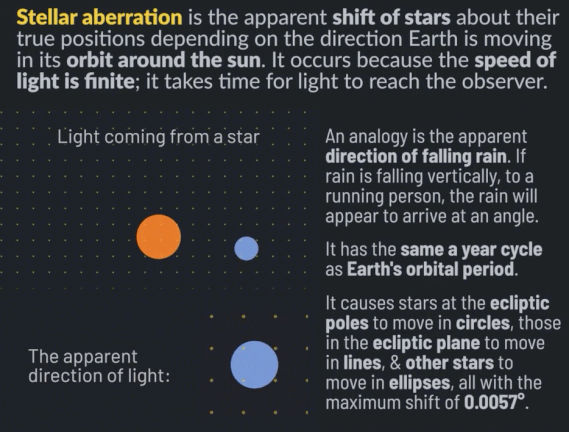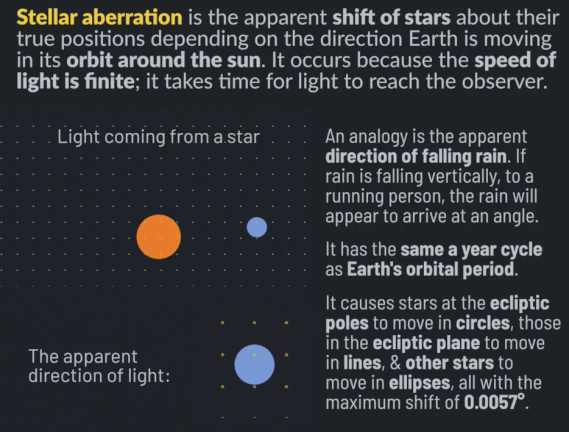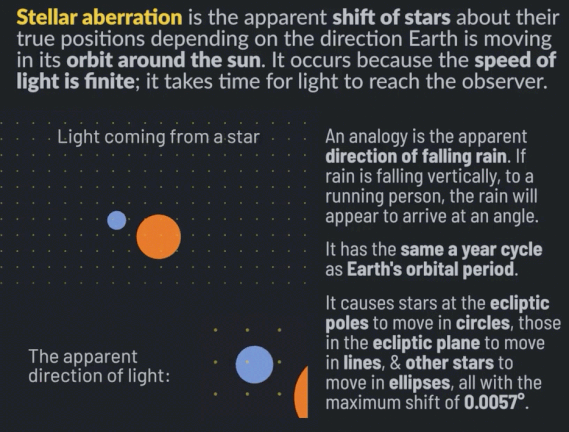
Stellar aberration is the apparent shift of stars about their actual positions, depending on the direction Earth is moving in its orbit around the sun. It occurs because the speed of light is finite; it takes time for light to reach the observer. Stellar aberration was discovered in 1727 by James Bradley. It was the first direct proof of heliocentrism, that Earth is in orbit around the sun.
An analogy to explain stellar aberration is the apparent direction of falling rain. If rain is falling vertically, to a person running in the rain, the rain will arrive at an angle. The rain will appear to originate not from straight up but slightly tilted toward the direction the person is running.
An analogy to explain stellar aberration is the apparent direction of falling rain. If rain is falling vertically, to a person running in the rain, the rain will arrive at an angle. The rain will appear to originate not from straight up but slightly tilted toward the direction the person is running.
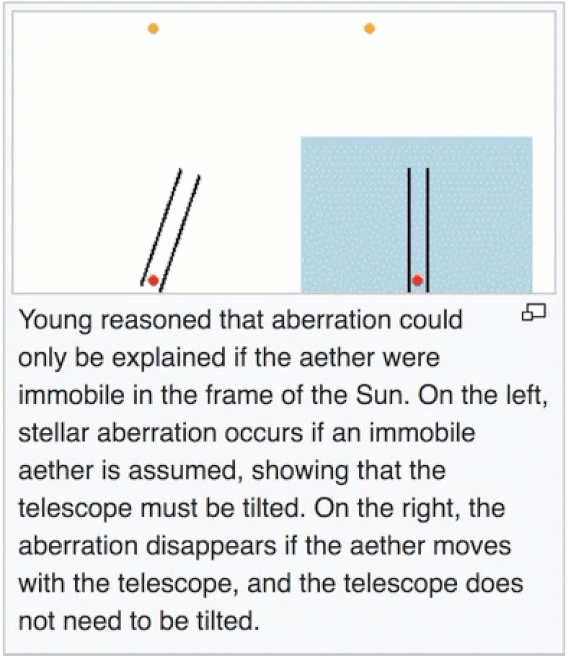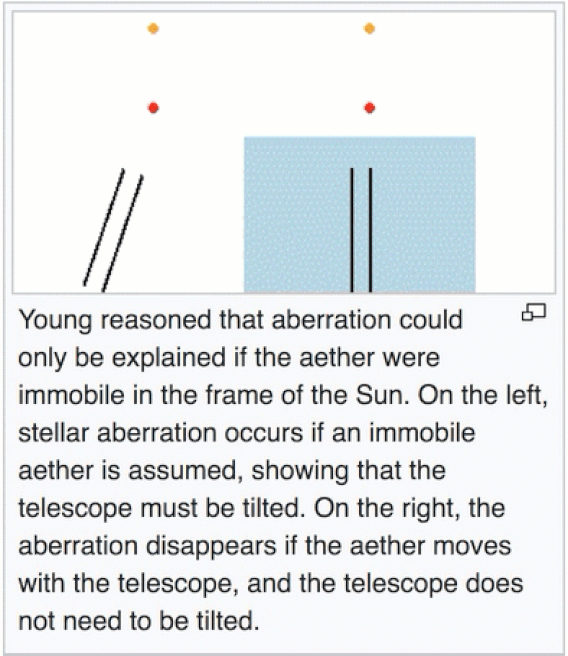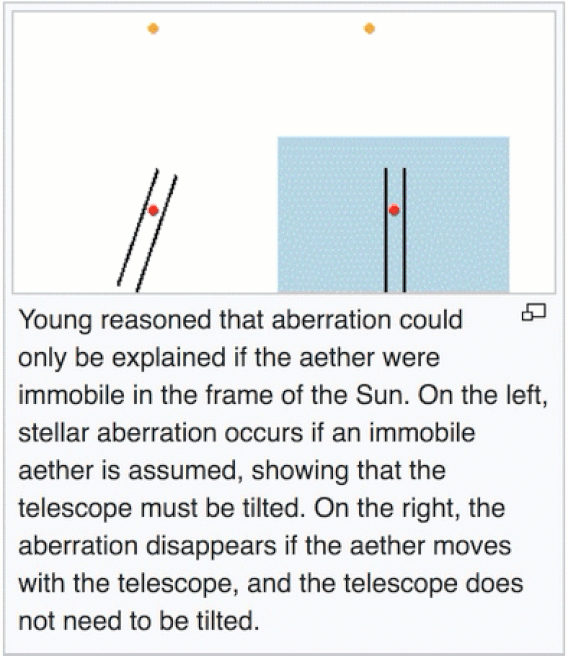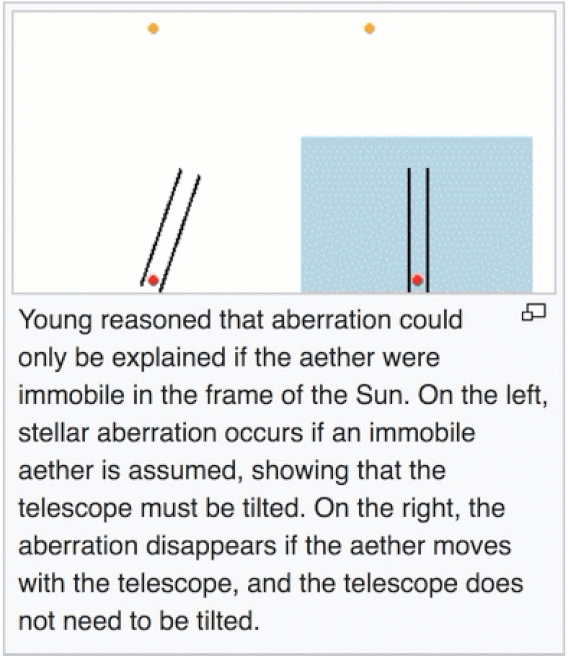
Stellar aberration is different from stellar parallax, which is the shift of nearby stars relative to more distant stars due to the change in Earth’s position around the sun. The magnitude of stellar parallax depends on the distance of the stars, while stellar aberration affects every star by the same maximum shift. Both phenomena are direct evidence of heliocentrism.
Stellar aberration has the same annual cycle as Earth’s orbital period. It causes stars at the ecliptic poles to move in circles, those in the ecliptic plane to move in lines, and other stars in between to move in ellipses. The maximum shift of stars due to stellar aberration is the speed of Earth’s motion around the sun divided by the speed of light, which is 0.00099365 radians or 20.49552 arcseconds.
Stellar aberration has the same annual cycle as Earth’s orbital period. It causes stars at the ecliptic poles to move in circles, those in the ecliptic plane to move in lines, and other stars in between to move in ellipses. The maximum shift of stars due to stellar aberration is the speed of Earth’s motion around the sun divided by the speed of light, which is 0.00099365 radians or 20.49552 arcseconds.
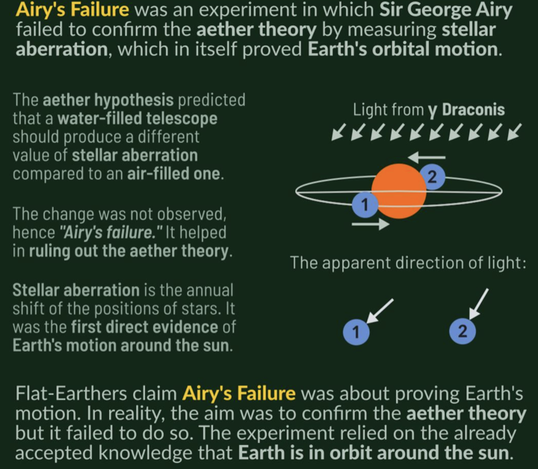
Airy’s Failure was an experiment performed in 1871 in which Sir George Biddell Airy failed to confirm the aether theory by measuring stellar aberration.
Flat-Earthers claim that the “failure” in “Airy’s Failure” is the failure of proving the motion of Earth. In reality, the experiment aimed to confirm the aether theory. The “failure” was in proving the aether theory. The experiment relied on the already accepted knowledge that Earth is in orbit around the sun.
The aether drag hypothesis predicted that a water-filled telescope should produce a different value of stellar aberration compared to an air-filled one. The change was not observed, hence the name “Airy’s failure.” The experiment helped in ruling out the aether theory.
Okay, now to the actual science, and the root of Airy’s real failure. His entire experiment was based on the false assumption that light required a medium through which to travel, commonly referred to at the time as “aether”. His experimental results were therefore skewed by that underlying false assumption, thus leading to yet another false conclusion, that the failure of starlight to act as predicted based on a heliocentric model must mean that the heliocentric model was false. In fact what his experiment really proved, which wouldn’t be scientifically explained for some time, was there was no such thing as aether and that light did NOT require a medium through which to travel.
**However, if you believe in the Aether (against all evidence), then you would conclude the Earth was stationary, even though the regular stellar aberration observations indicate that it is not stationary.
Flat-Earthers claim that the “failure” in “Airy’s Failure” is the failure of proving the motion of Earth. In reality, the experiment aimed to confirm the aether theory. The “failure” was in proving the aether theory. The experiment relied on the already accepted knowledge that Earth is in orbit around the sun.
The aether drag hypothesis predicted that a water-filled telescope should produce a different value of stellar aberration compared to an air-filled one. The change was not observed, hence the name “Airy’s failure.” The experiment helped in ruling out the aether theory.
Okay, now to the actual science, and the root of Airy’s real failure. His entire experiment was based on the false assumption that light required a medium through which to travel, commonly referred to at the time as “aether”. His experimental results were therefore skewed by that underlying false assumption, thus leading to yet another false conclusion, that the failure of starlight to act as predicted based on a heliocentric model must mean that the heliocentric model was false. In fact what his experiment really proved, which wouldn’t be scientifically explained for some time, was there was no such thing as aether and that light did NOT require a medium through which to travel.
**However, if you believe in the Aether (against all evidence), then you would conclude the Earth was stationary, even though the regular stellar aberration observations indicate that it is not stationary.
The important thing to conclude from these experiments with stellar aberration is that the ether is not dragged around the earth. If it were, the ether would be at rest with respect to the earth, the telescope would not have to be tilted and there would be no aberration at all. That is, the ether would be moving (with the earth) to the right with speed v, so there would be no need to correct for the earth's motion through the ether.

The Sagnac effect occurs to a pair of light beams traveling in a circuit in the opposite direction. If the circuit itself is rotating, then the beams will complete the circuit in different duration. The effect was first demonstrated by Georges Sagnac in 1913.
After discovering this effect, Sagnac incorrectly used the results as proof of the aether’s existence, and today’s flat-Earthers use it as “evidence” of stationary Earth. In reality, Sagnac was not aware that the effect is consistent with Einstein’s theory of relativity. And if the effect really proved aether, then optical gyroscopes are impossible.
The Sagnac effect is used as the basis of optical gyroscopes, including fiber-optic gyroscopes and ring-laser gyroscopes. In an optical gyroscope, a pair of light beams are made to travel in a circuit in the opposite direction. Because light travels at a constant speed, irrespective of the transmitter’s speed, then if the gyroscope is rotated, a beam of light will complete the circuit sooner than the other. From the difference, we can measure the rotating motion of the gyroscope.
After discovering this effect, Sagnac incorrectly used the results as proof of the aether’s existence, and today’s flat-Earthers use it as “evidence” of stationary Earth. In reality, Sagnac was not aware that the effect is consistent with Einstein’s theory of relativity. And if the effect really proved aether, then optical gyroscopes are impossible.
The Sagnac effect is used as the basis of optical gyroscopes, including fiber-optic gyroscopes and ring-laser gyroscopes. In an optical gyroscope, a pair of light beams are made to travel in a circuit in the opposite direction. Because light travels at a constant speed, irrespective of the transmitter’s speed, then if the gyroscope is rotated, a beam of light will complete the circuit sooner than the other. From the difference, we can measure the rotating motion of the gyroscope.
Did Airy prove the stars are stationary.
Michelson, Morley, Airy and even Einstein himself who at the end said "I have come to believe that the earth motion cannot be observed by any optical instruments." End quote
Michelson, Morley, Airy and even Einstein himself who at the end said "I have come to believe that the earth motion cannot be observed by any optical instruments." End quote
“While I was thinking of this problem in my student years, I came to know the strange result of Michelson’s experiment. Soon I came to the conclusion that our idea about the motion of the Earth with respect to the ether is incorrect, if we admit Michelson’s null result as a fact. This was the first path which led me to the special theory of relativity. Since then I have come to believe that the motion of the Earth cannot be detected by any optical experiment, though the Earth is revolving around the Sun.”
What Einstein meant by the “optical experiment” is the Michelson-Morley experiment. As you know, before his Theory of Relativity, scientists hypothesized the Aether theory to explain why light can propagate through space, unlike other types of waves that require a medium.
The Michelson-Morley experiment was unable to confirm the existence of Aether. They cannot find the difference of light speed traveling at different angles, even though the Earth is in motion. It is what Einstein had in mind.
I hope you are open to truth. It is not my intention to convert any flat earther to the globe, I just like to know and share truth. So I would encourage you to not share this quote out of context, now you have seen (and can research for yourself) the true origin and meaning of the full quote taken in context.
"Common sense is that layer of prejudice laid down in the mind prior to the age of eighteen."
-Albert Einstein
What Einstein meant by the “optical experiment” is the Michelson-Morley experiment. As you know, before his Theory of Relativity, scientists hypothesized the Aether theory to explain why light can propagate through space, unlike other types of waves that require a medium.
The Michelson-Morley experiment was unable to confirm the existence of Aether. They cannot find the difference of light speed traveling at different angles, even though the Earth is in motion. It is what Einstein had in mind.
I hope you are open to truth. It is not my intention to convert any flat earther to the globe, I just like to know and share truth. So I would encourage you to not share this quote out of context, now you have seen (and can research for yourself) the true origin and meaning of the full quote taken in context.
"Common sense is that layer of prejudice laid down in the mind prior to the age of eighteen."
-Albert Einstein
- A REFINEMENT OF THE MICHELSON-MORLEY EXPERIMENT
- September 1926
- Roy J. Kennedy
- https://www.pnas.org/content/12/11/621
- Direct PDF Download: A REFINEMENT OF THE MICHELSON-MORLEY EXPERIMENT
- A Repetition of the Michelson-Morley Experiment Using Kennedy’s Refinement
- November 1927
- https://journals.aps.org/pr/abstract/10.1103/PhysRev.30.692
- Direct PDF Download: A Repetition of the Michelson-Morley Experiment Using Kennedy’s Refinement
- Repetition of the Michelson-Morley Experiment
- January 1929
- A. A. M
MIICHELSON, Dr. F. G. PEASE, and F. PEARSON - https://www.nature.com/articles/123088a0
- Direct PDF Download: Repetition of the Michelson-Morley Experiment
- A Modern Michelson-Morely Experiment Using Actively Rotated Optical Resonators
- Modern Michelson-Morley experiment using cryogenic optical resonators
- February 2008
- Holger Muller, Sven Herrmann, Claus Braxmaier, Stephan Schiller, and Achim Peters
- https://arxiv.org/pdf/physics/0305117.pdf
- Direct PDF Download: Modern Michelson-Morley experiment using cryogenic optical resonators
- Laboratory Test of the Isotropy of Light Propagation at the 10−17 Level
- August 2009
- Ch. Eisele, A. Yu. Nevsky, and S. Schiller
- https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.103.090401
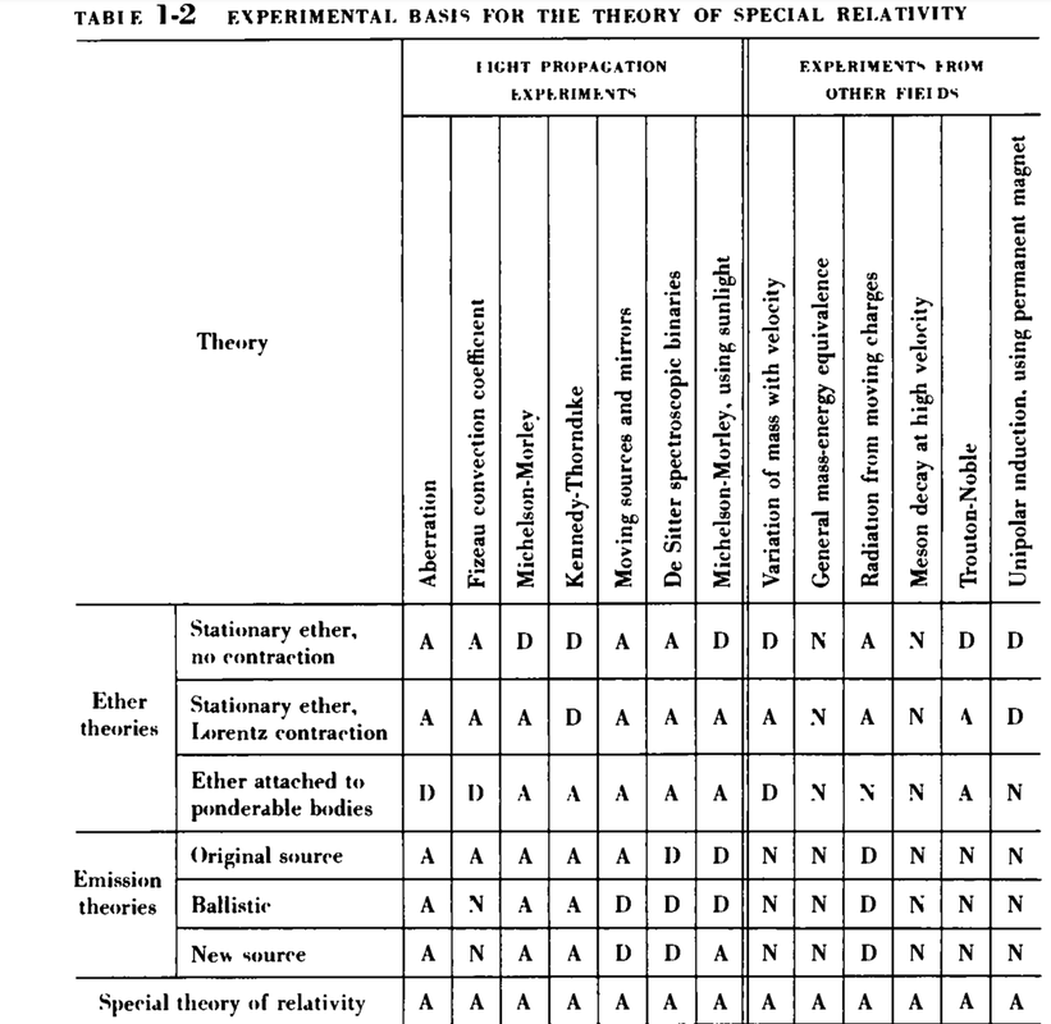
The following experiments support Special Relativity and the constant speed of light. Where is your evidence for your interpretation?
Cherenkov radiation is a form of energy that we can perceive as a blue glow emitted when the electrically charged particles that compose atoms (i.e. electrons and protons) are moving at speeds faster than that of light in a specific medium.
Cherenkov radiation is a form of energy that we can perceive as a blue glow emitted when the electrically charged particles that compose atoms (i.e. electrons and protons) are moving at speeds faster than that of light in a specific medium.
- Kosteleck and Mewes, “Signals for Lorentz violation in electrodynamics”, Phys. Rev. D66, 056005 (2002).A review of various limits, terrestrial and astrophysical.
- Mueller, “Testing Lorentz invariance by the use of vacuum and matter filled cavity resonators”, Phys. Rev. D71, 045004 (2005).A review article.
- Miller, H., P.L. Stanwix, M.E. Tobar, E. Ivanov, P. Wolf, S. Herrmann, A. Senger, E. Kovalchuk, A. Peters, “Relativity tests by complementary rotating Michelson-Morley experiments”, arXiv:0706.2031v1 [physics.class-ph].By combining results from two interferometers made of different materials, located in different hemispheres, rotating on tables, they are able to put limits on more parameters of the SME than otherwise. They have also improved both the statistics and systematic errors of the individual interferometers.
- Nguyen, H.H., “CPT results from KTeV”, (2001). arXiv:hep-ex/0112046.-
- Schwingenheuer, B. et al., “CPT tests in the neutral kaon system”, Phys. Rev. Lett., 74, pg 4376–4379, (1995).-
- Gurzadyan et al., “Probing the Light Speed Anisotropy with respect to the Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation Dipole”, Mod. Phys. Lett., 2005, v.20, pg 19. arXiv:astro-ph/0410742.-
- Hughes, V.W., Grosse Perdekamp, M., Kawall, D., Liu, W., Jungmann, K., and zu Pulitz, G., “Test of CPT and Lorentz Invariance from Muonium Spectroscopy”, Phys. Rev. Lett., 87, 111804-1-4, (2001). arxiv:hep-ex/0106103.-
- Bluhm, R., Kosteleck, V.A., and Lane, C.D.,“CPT and Lorentz tests with muons”, Phys. Rev. Lett., 84, pg 1098–1101, (2000). arXiv:hep-ph/9912451.-
- Carey, R.M. et al., “New Measurement of the Anomalous Magnetic Moment of the Positive Muon”, Phys. Rev. Lett., 82, pg 1632–1635, (1999).-
- R. Grieser, R. Klein, G. Huber, S. Dickopf, I. Klaft, P. Knobloch, P. Merz, F. Albrecht, M. Grieser, D. Habs, D. Schwalm and T. Kaehl, “A test of special relativity with stored lithium ions”, Appl. Phys. B59, no. 2, pg 127 (1994).Klein et al., Zeitschrift fuer Physik A 342, pg 455 (1992).Saathoff, G., Karpuk, S., Eisenbarth, U., Huber, G., Krohn, S., Horta, R.M., Reinhardt, S., Schwalm, D., Wolf, A., and Gwinner, G., “Improved Test of Time Dilation in Special Relativity”, Phys. Rev. Lett., 91, 190403, (2003).G. Saathoff, S. Reinhardt, H. Buhr, L.A. Carlson, D. Schwalm, A. Wolf, S. Karpuk, C. Novotny, G. Huber, and G. Gwinner, Can. J. Phys./Rev. can. phys. 83(4): pg 425–434 (2005)(Saathof's Ph.D. thesis, 2002) http://www.mpi-hd.mpg.de/ato/homes/saathoff/diss-saathoff.pdf(Reinhardt's Ph.D. thesis, 2005) http://archiv.ub.uni-heidelberg.de/volltextserver/volltexte/2005/5934/pdf/doktorarbeit_sreinhardt.pdfThis is an incredibly clever experiment using 7Li+ ions in a storage ring, synchronizing a single laser to a 2-level transition via Doppler shifts in both directions. The fractional accuracy in frequency is 10−9, and the limit on deviation from the relativistic formula is 2.2�10−7 for speeds a substantial fraction of c.
- Lane, C.D., “Probing Lorentz violation with Doppler-shift experiments”. arXiv:hep-ph/0505130.-
- Mittleman, R.K., Ioannou, I.I., Dehmelt, H.G., and Russell, N., “Bound on CPT and Lorentz symmetry with a trapped electron”, Phys. Rev. Lett., 83, pg 2116–2119, (1999).-
- Gabrielse, G., Khabbaz, A., Hall, D.S., Heimann, C., Kalinowsky, H., and Jhe, W., “Precision mass spectroscopy of the antiproton and proton using simultaneously trapped particles”, Phys. Rev. Lett., 82, pg 3198–3201, (1999).-
- Dehmelt, H.G., Mittleman, R.K., van Dyck Jr, R.S., and Schwinberg, P., “Past electron positron g-2 experiments yielded sharpest bound on CPT violation”, Phys. Rev. Lett., 83, pg 4694–4696, (1999). arXiv:hep-ph/9906262.-
- Auerbach et al. (LSND Collaboration), “Test of Lorentz violation in Anti-νμ → Anti-νe oscillations”. Phys. Rev. D 72, 076004 (2005).These neutrino oscillations display no significant sidereal variation.Note, however, that the LSND results have been a puzzle for several years, as they appear to be inconsistent with other experiments. Just recently they were directly contradicted by the Mini-BooNE results from Fermilab (May 2007, no reference yet).
- Kosteleck and Mewes, “Lorentz violation and short-baseline neutrino experiments”, Phys. Rev. D70, 076002 (2004).Using the published results of the Liquid Scintillator Neutrino Detector (LSND) experiment, an estimated nonzero value (3 1)10−19 GeV for a combination of coefficients for Lorentz violation is obtained. This lies in the range expected for effects originating from the Planck scale in an underlying unified theory.Note, however, that the LSND results have been a puzzle for several years, as they appear to be inconsistent with other experiments. Just recently they were directly contradicted by the Mini-BooNE results from Fermilab (May 2007, no reference yet).
- Walsworth, Bear, Humphrey, Mattison, Phillips, Stoner, and Vessot, “New Clock Comparison Searches for Lorentz and CPT Violation”, arxiv:physics/0007063 (2000).Bear, D., Stoner, R.E., Walsworth, R.L., Kosteleck, V.A., and Lane, C.D., “Limit on Lorentz and CPT violation of the neutron using a two-species noble-gas maser”, Phys. Rev. Lett., 85, pg 5038–5041, (2000). arXiv:physics/0007049.Bear, D., Stoner, R.E., Walsworth, R.L., Kosteleck, V.A., and Lane, C.D., “Erratum: Limit on Lorentz and CPT Violation of the Neutron Using a Two-Species Noble-Gas Maser”, Phys. Rev. Lett., 89, 209902, (2002).Cane, Bear, Phillips, Rosen, Smallwood, Stoner, and Walsworth, “Bound on Lorentz and CPT Violating Boost Effects for the Neutron”, Phys. Rev. Lett. 93, 230801 (2004).Search for sidereal variation in the frequency difference between co-located 129Xe and 3He Zeeman masers sets the most stringent limits to date on leading order Lorentz and CPT violation. By locating the two masers in the same enclosure they eliminate many systematic errors, and are looking at variations at the level of 100 nHz (10−7 Hz !).
- Kosteleck, V.A., and Lane, C.D., “Constraints on Lorentz violation from clock-comparison experiments”, Phys. Rev. D, 60, 116010, (1999). arXiv:hep-ph/9908504.-
- Bertolami, O., and Rosa, J.G., “New bounds on cubic Lorentz-violating terms in the fermionic dispersion relation”, Phys. Rev. D, 71, 097901. arXiv:hep-ph/0412289.-
- Berglund, C.J. et al., “New Limits on Local Lorentz Invariance from Hg and Cs Magnetometers”, Phys. Rev. Lett., 75, 1879, (1995).-
- Phillips, D.F., Humphrey, M.A., Mattison, E.M., Stoner, R.E., Vessot, R.F.C., and Walsworth, R.L., “Limit on Lorentz and CPT violation of the proton using a hydrogen maser”, Phys. Rev. D, 63, 111101, (2001). arXiv:physics/0008230.Humphrey et al., “Testing CPT and Lorentz Symmetry with Hydrogen Masers”, Phys. Rev. A68, 063807 (2003). arXiv:physics/0103068.-
- Ellis, J.R., Farakos, K., Mavromatos, N.E., Mitsou, V.A., and Nanopoulos, D.V., “Astrophysical probes of the constancy of the velocity of light”, Astrophys. J., 535, 139–151, (2000). arXiv:astro-ph/9907340.-
- Ellis, J.R., Mavromatos, N.E., Nanopoulos, D.V., and Sakharov, A.S., “Quantum-gravity analysis of gamma-ray bursts using wavelets”, Astron. Astrophys., 402, 409–424, (2003). arXiv:astro-ph/0210124.-
- Biller, S.D., Breslin, A.C., Buckley, J., Catanese, M., Carson, M., Carter-Lewis, D.A., Cawley, M.F., Fegan, D.J., Finley, J.P., Gaidos, J.A., Hillas, A.M., Krennrich, F., Lamb, R.C., Lessard, R., Masterson, C., McEnery, J.E., McKernan, B., Moriarty, P., Quinn, J., Rose, H.J., Samuelson, F., Sembroski, G., Skelton, P., and Weekes, T.C., “Limits to quantum gravity effects from observations of TeV flares in active galaxies”, Phys. Rev. Lett., 83, 2108–2111, (1999). arXiv:gr-qc/9810044.-
- Boggs, S.E., Wunderer, C.B., Hurley, K., and Coburn, W., “Testing Lorentz Non-Invariance with GRB021206”, (2003). arXiv:astro-ph/0310307.-
- Ellis et al., “Robust Limits on Lorentz Violation from Gamma-Ray Bursts”, arXiv:astro-ph/0510172 (2005).If the speed of light has an energy dependence c(E) ~ c0(1 − E/M), a limit on M is obtained: M > 0.91016 GeV/c2.
- Kosteleck and Mewes, “Cosmological Constraints on Lorentz Violation in Electrodynamics”, Phys. Rev. Lett., 87, no. 25, 251304 (2001).Certain coefficients for Lorentz violation are bounded to less than 310−32.
- Lehnert, R., and Potting, R., “The Cerenkov effect in Lorentz-violating vacua”, Phys. Rev. D, 70, 125010, (2004). arXiv:hep-ph/0408285 .Lehnert, R., and Potting, R., “Vacuum Cerenkov radiation”, Phys. Rev. Lett., 93, 110402, (2004). arXiv:hep-ph/0406128.-
- Coleman, S.R., and Glashow, S.L., “Cosmic ray and neutrino tests of special relativity”, Phys. Lett. B, 405, 249-252, (1997). http://arXiv.org/abs/hep-ph/9703240.Coleman, S.R., and Glashow, S.L., “Evading the GZK cosmic-ray cutoff”, (1998). arXiv:hep-ph/9808446.Coleman, S.R., and Glashow, S.L., “High-energy tests of Lorentz invariance”, Phys. Rev. D, 59, 116008, (1999). arXiv:hep-ph/9812418.-
- Greisen, K., “End to the cosmic ray spectrum?”, Phys. Rev. Lett., 16, pg 748–750, (1966).Zatsepin, G.T., and Kuzmin, V.A., “Upper limit of the spectrum of cosmic rays”, J. Exp. Theor. Phys. Lett., 4, pg 78–80, (1966).The original GZT papers.